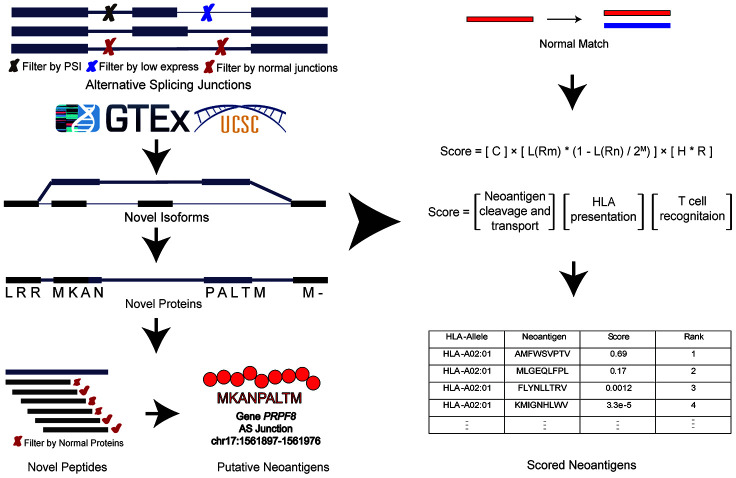
Figure 2.
The computational pipeline of ASNEO for identification of AS neopeptides. The ASNEO accepted splice junctions detected by STAR, and then filtered low expressed junctions, low psi junctions, and Normal Junctions. Next, ASNEO inserted the filtered junctions into reference isoforms to generate novel isoforms and translated the novel isoforms to novel proteins by one-frame translation from the translation start site to the stop codon. The filtered novel proteins then were chopped up to 8-11-mer peptides, which were filtered by Normal Proteins. The bind ranks of remained peptides to HLA were calculated by NetMHCpan-4.0 and those peptides whose %rank<2 were considered as putative neopeptides. In addition, ASNEO integrated an immune score to evaluate the immunogenicity of putative neopeptides with several features, including the mutant peptide-MHC %rank, the normal peptide-MHC %rank, the number of mismatches between the mutant peptide and normal peptide as well as the cleavage probability, the TAP transport efficiency, the hydrophobicity score and the T cell recognition probability of mutant peptide.