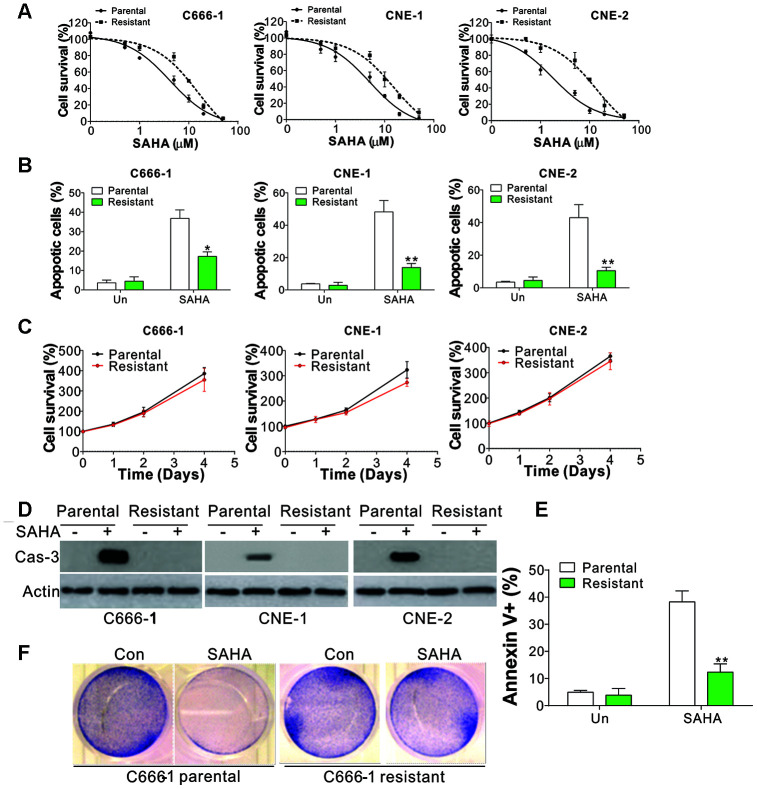
Figure 1.
SAHA-tolerant NPC cell exhibits apoptosis defects. (A) The cell viability in parental and SAHA-tolerant phenotype upon different concentrations of SAHA treatment for 24 h was analyzed by MTS assay. (B) The apoptosis of parental and SAHA-tolerant phenotype subjected to 4 μmol/L of SAHA for 24 h. (C) The proliferation of parental and SAHA-tolerant phenotype was analyzed by MTS assay upon different time points. (D) The cleaved Cas-3 expression in parental and SAHA-tolerant phenotype subjected to 4 μmol/L of SAHA for 24 h. (E) The parental and SAHA-tolerant C666-1 cells were subjected to 4 μmol/L of SAHA for 24 h, and stained with Annexin V and PI, followed by flow cytometry analysis. (F) The crystal violet staining of parental and SAHA-tolerant C666-1 cells was subjected to 4 μmol/L of SAHA for 24 h. Each experiment was performed for 3 times. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01.