Figure 5.
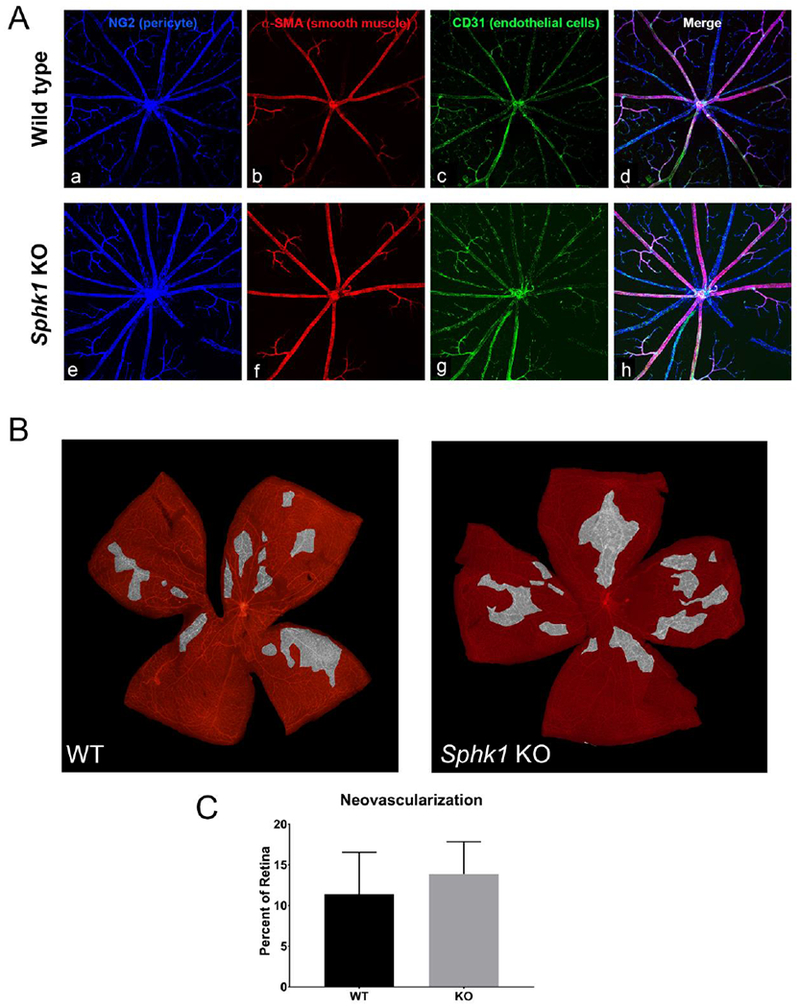
Vascular adherens junctions and neovascular potential are not affected by a deletion of Sphk1. A) Flat mounted retina from WT (a-d) and Sphk1 KO (e-h) mice were probed for pericyte coverage (a and e), smooth muscle cell coverage of arterioles (b and f), and endothelial cells (c and g). No differences were observed. B) Retinopathy of prematurity model for neovascularization showed no difference between WT or Sphk1 KO mouse retinas. Areas highlighted in grey have a high density of NV tufts, formed in response to the hypoxic environment after the mice are returned to normoxia for 5 days. C) Quantification of NV tuft areas after ROP show no major difference in NV between Sphk1 KO or WT. (n=7, two-tailed Student’s t-test, α=0.05, error bars are SD).
