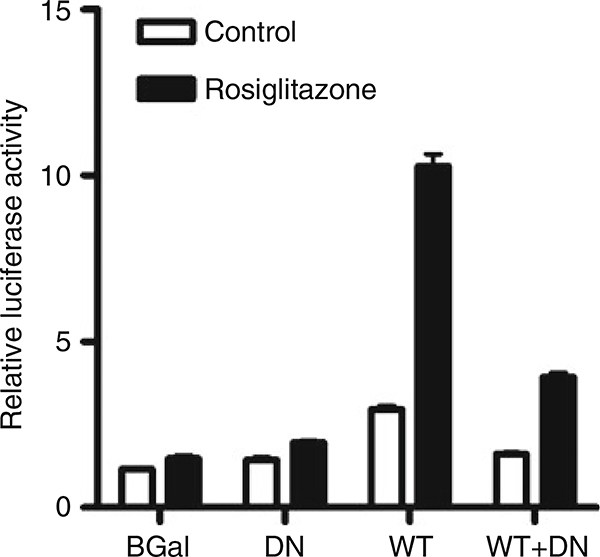
Fig. 2.
Determination of PPARγ transcriptional activity in cells infected with wild-type (WT) and dominant-negative (DN) adenoviruses. Cells were infected with control (β-Gal), DN, WT, or both DN and WT adenoviruses at an MOI of 1.0 each. Control (β-Gal) adenovirus was used to adjust the total viral load to 2.0 MOI when necessary. After 4 h, the cells were transfected with ACO-PPRE-luc and pRL-TK reporter plasmids, and incubated for 24 h. Cells were treated with rosiglitazone (1 μM) or vehicle, and 24 h later firefly and Renilla luciferase activities were measured. Rosiglitazone caused a marked increase in PPARγ activity in the WT cells, which was reduced in presence of the DN mutant.