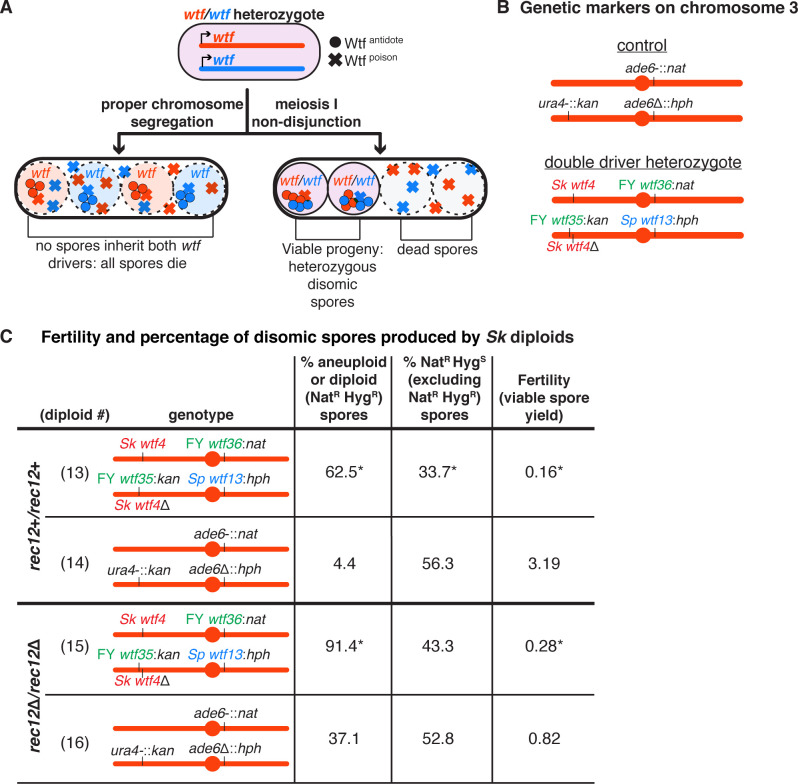
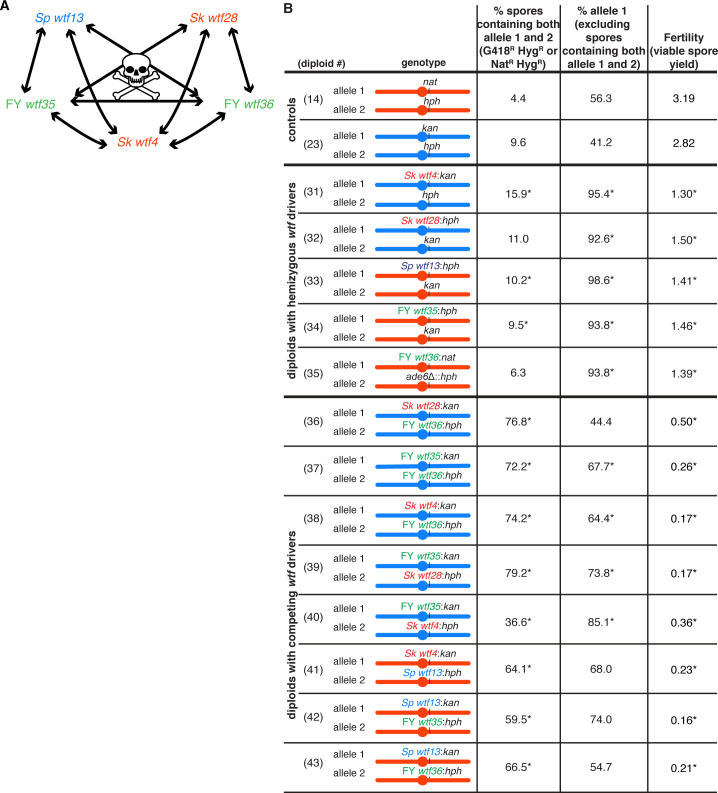
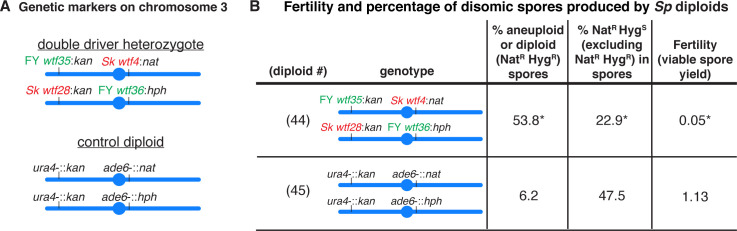
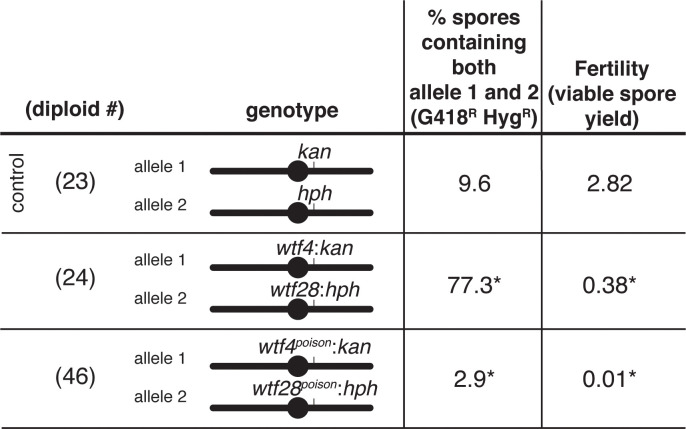
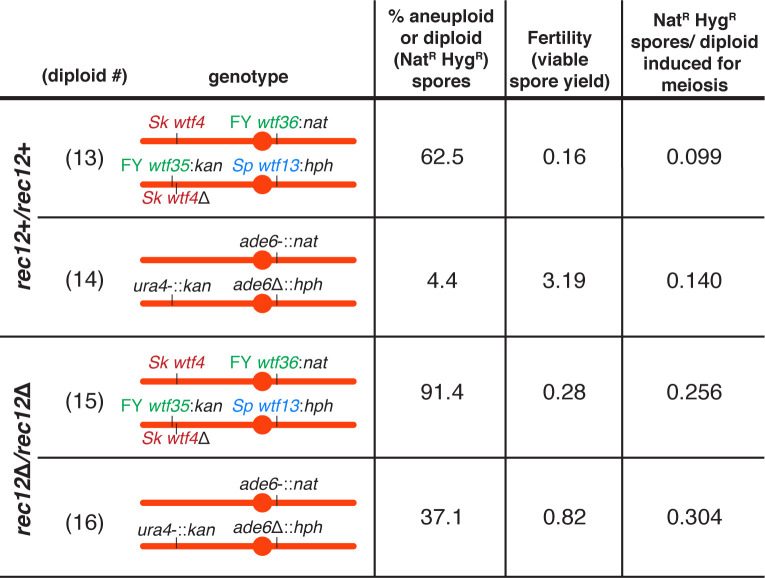
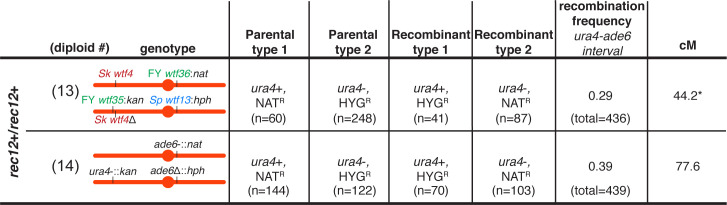
Figure 2. A high fraction of viable spores are disomic in Sk strains with wtf competition at two loci.
(A) Model for a diploid heterozygous for distinct wtf meiotic drivers. Spores are destroyed by any wtf driver that they do not inherit from the diploid progenitor cell. Meiosis I chromosome missegregation is one mechanism by which spores can inherit wtf alleles on competing haplotypes and survive. (B) Schematic of the genetic markers at ura4 and ade6 in the control diploid and the wtf transgenes inserted at ura4 and ade6 in Sk chromosome 3 in the double driver heterozygote. wtf genes from the Sp, Sk, and FY29033 strains are depicted in blue, red, and green, respectively. The wtf drivers shown here drive when heterozygous and do not counteract the effect of the other drivers (see Figure 2—figure supplement 1). (C) Phenotypes of the double driver heterozygote or control diploid in rec12+ (top) and rec12Δ (bottom) strain backgrounds. We expect NatR HygS spores to be present at 50% in the viable population. A significant departure from the expected 50% indicates drive favoring the overrepresented allele. For statistical analyses, the frequency of disomic spores, allele transmission, and fertility in the double driver heterozygotes was compared to the control diploids. Diploid 13 was compared to control diploid 14, and diploid 15 was compared to control diploid 16. * indicates p-value<0.05 (G-test [allele transmission and NatR HygR spores] and Wilcoxon test [fertility]). The data for diploid 14 were previously published in Bravo Núñez et al., 2020. Raw data can be found in Figure 2—source data 1 and Figure 2—source data 2.