Extended Data Fig. 4. Arabidopsis TREX-2 components and sac3 mutant alleles.
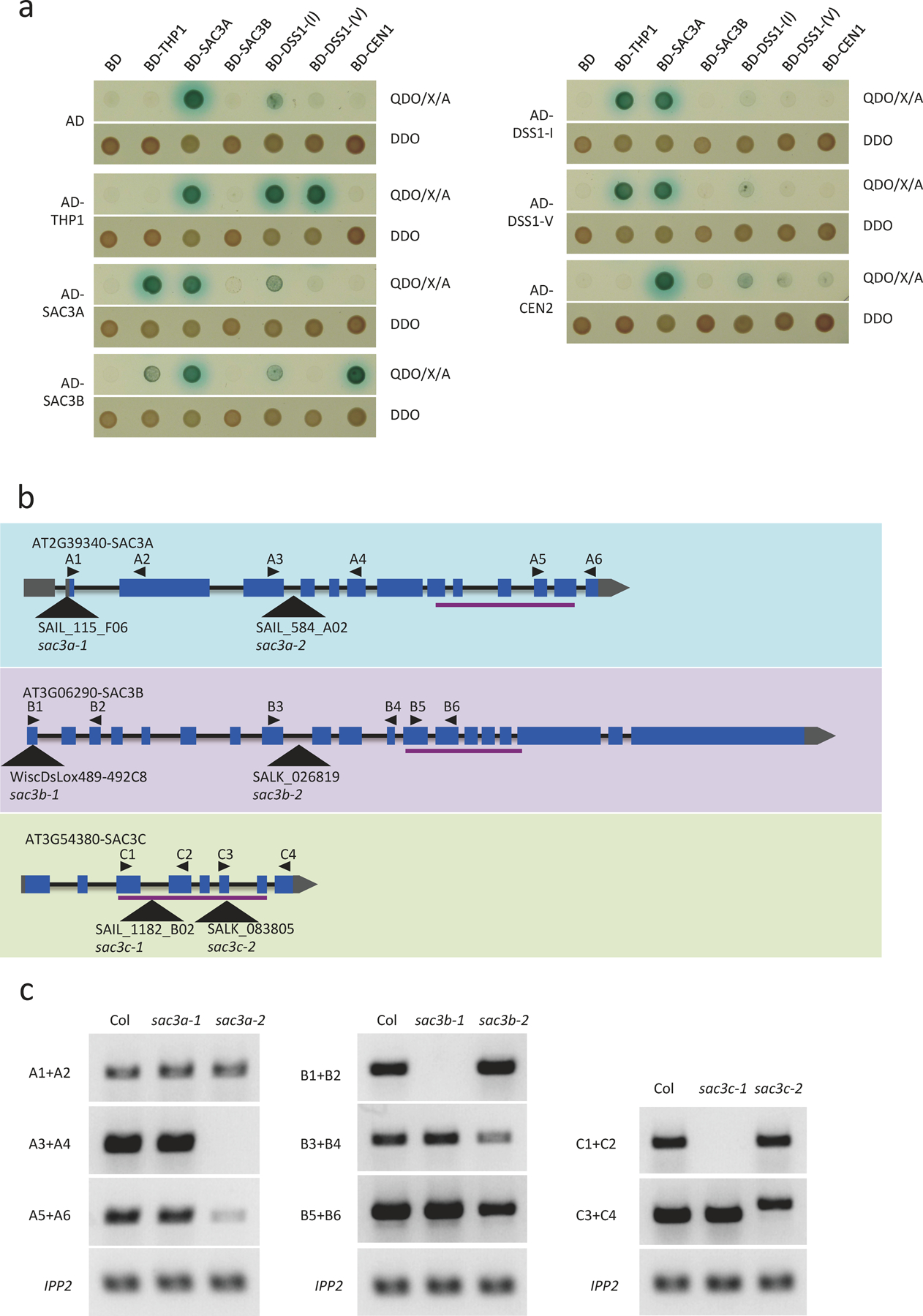
(a) Yeast two-hybrid assays to test interactions among TREX-2 components (THP1, SAC3A, SAC3B, DSSI-(I), DSSI-(V), CEN1, and CEN2). The empty vectors AD and BD were included as negative controls. After mating, diploid yeast cells containing both the bait and prey plasmids grew on SD-Trp/-Leu (DDO) medium, and diploid yeast cells in which the bait and prey proteins interacted grew into blue colonies on SD-Trp/-Leu/-His/-Ade+X-α-gal Aureobasidin A (QDO/X/A) medium. The experiment was repeated two times with similar results. (b) Diagrams of SAC3A, B, and C genes showing the different mutant alleles. Triangles indicate positions of T-DNA insertions. Black arrows indicate primers used for RT-PCR. Lines below the gene models indicate conserved protein domains in homologous proteins. (c) RT-PCR analyses of SAC3 gene expression in different sac3 mutants. The primers used are shown as black arrows in (b). The experiment was repeated two times with similar results.
