Figure 6.
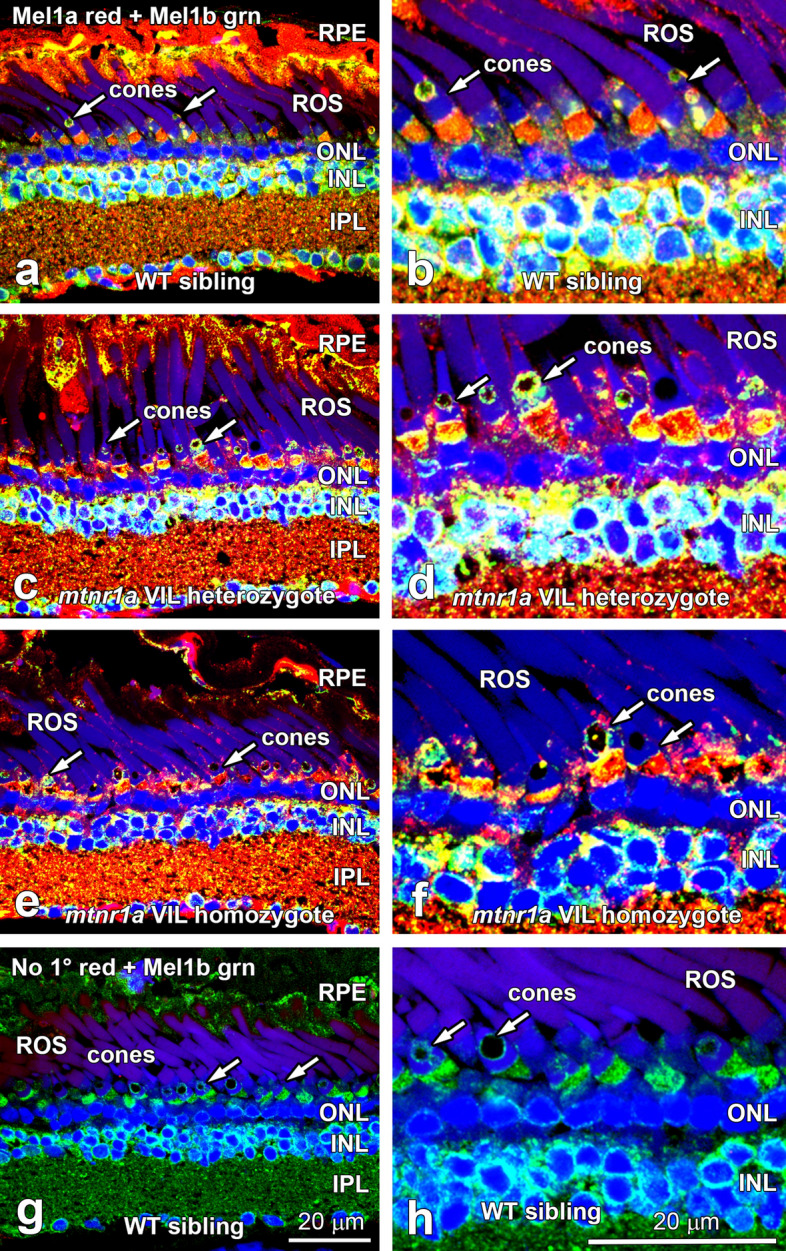
Retinas of heterozygous and homozygous mtnr1a VIL mutant tadpoles display Mel1a protein expression at intensities similar to WT siblings. Double-label confocal immunohistochemistry (IHC) of (a,b) WT, (c,d) F2 VIL heterozygous, and (e,f) F2 VIL homozygous tadpole head paraffin sections was performed with antibodies to X. laevis Mel1a (red label) and Mel1b (green label) melatonin receptors. Panels on the right are higher magnifications of areas in panels on the left side of the figure. Mel1a receptor fluorescent signal intensity and location appears to be similar in animals of all three genotypes. The Mel1a receptor is expressed in RPE, rod and cone photoreceptors (arrows), and inner retinal neurons. The Mel1a and Mel1b receptors display an expression pattern different from each other, although there are areas in which the red and green labels merge as a yellow label, suggestive of co-expression and/or very close proximity to each other. (g,h) WT retina sections processed for IHC with Mel1b antibodies, but without Mel1a antibodies (No 1° red) display specific immunofluorescence for Mel1b (green), but not for Mel1a (red). RPE retinal pigment epithelium, ROS rod outer segments, ONL outer nuclear layer, INL inner nuclear layer, IPL inner plexiform layer, arrows; rod photoreceptor inner segments. Magnification bars = 20 µm.
