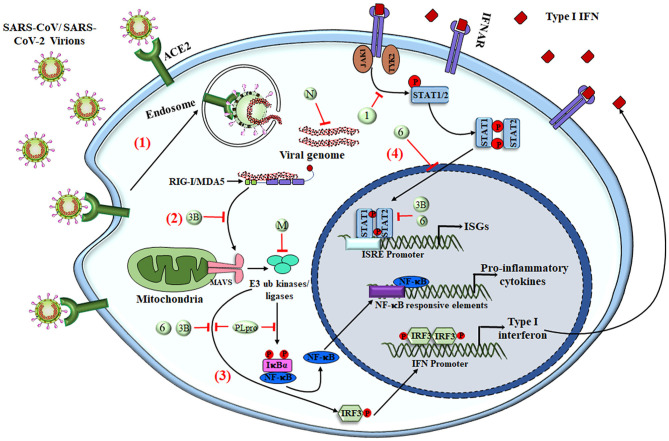
Figure 3.
SARS-CoV-mediated evasion of host innate immune response. The viral antigens are recognized via different PRRs to elicit the innate immune response. (1) Upon interaction of the virus with surface PRRs or the specific receptor, the particles are endocytosed into the cytosol and are then recognized by cytosolic PRRs like RIG-I and MDA5. (2) The viral genome, along with different proteins, interacts with MAVS and initiates NF-κB activation via triggering a signaling cascade that involves numerous E3 ubiquitin kinases and ligases. (3) Upon translocation into the nucleus, activated NF-κB acts as a transcriptional activator for numerous pro-inflammatory cytokines with an NF-κB-response element. The IFN-regulatory factor 3 (IRF3), upon phosphorylation via ubiquitin kinases, homodimerizes and moves inside the nucleus to activate the transcription of Type I IFNs. (4) Type I IFNs have both autocrine and paracrine mechanisms to activate the JAK–STAT signaling pathway via IFNα/β receptor (IFNAR), followed by phosphorylation of STAT1 and STAT2 via cytoplasmic protein JAK1 and TYK2 kinases. STAT1 & STAT2 heterodimers translocate into the nucleus and are recruited for transcription of the IFN-stimulated gene having an IFN-stimulated response element (ISRE) present on their promoter. SARS-CoV and other coronaviruses have found many ways to inhibit the signaling cascade by utilizing either the structural proteins (M and N protein) or NSPs (NSP1, NSP3b, and NSP6 along with PLpro), shown as numbers and letters in the figure. Together, the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and type I IFNs tries to create an antiviral immune microenvironment that controls viral synthesis and infection, but the viruses have deployed various strategies to shut down these signaling pathways to counteract the immune response. RIG-I, Retinoic acid-Inducible Gene I protein; MDA5, Melanoma Differentiation-Associated protein 5; MAVS, Mitochondrial antiviral-signaling protein; M, Membrane protein; N, Nucleocapsid; IFNAR, IFNα/β receptor; ISGs, IFN-stimulated genes; ISRE, IFN-stimulated response element.