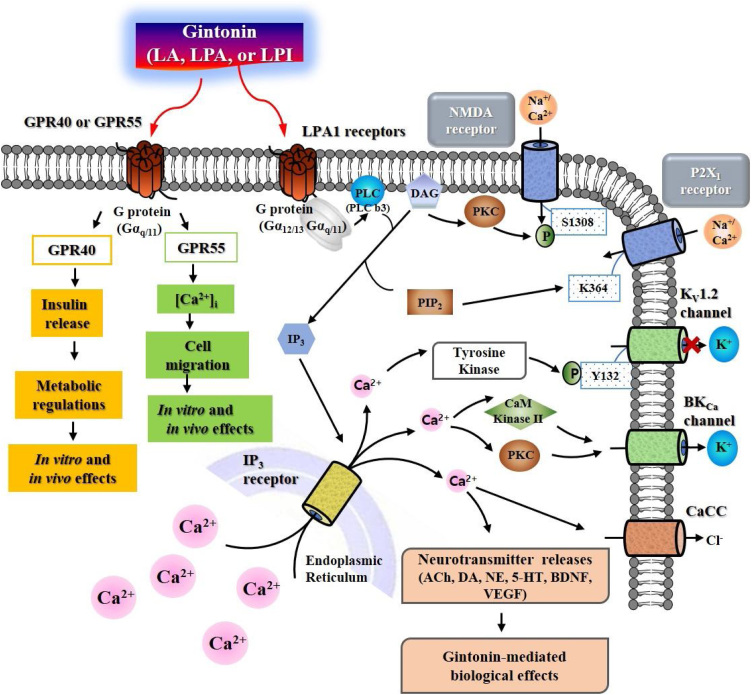
Fig. 2.
Signal transduction of ginseng gintonin on the mammalian cell plasma membrane via LPA receptors, GPR40, and GPR55. Gintonin activates LPA GPCRs, GPR40 and GPR55, respectively, which can lead to intracellular responses through the regulations of ion channels and receptors.18 In nervous system, gintonin-mediated signaling transduction pathway can be also coupled to neurotransmitter (i.e., acetylcholine, dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin) release for intercellular communications and to stimulations of BDNF and VEGF releases.18 The released neurotransmitters and neurotrophic factors further regulate their respective receptors to exhibit ginseng gintonin-mediated in vivo biological effects. Thus, in vivo biological effects of ginseng gintonin might be achieved via LPA receptors, GPR40, and/or GPR55 and indirectly via activations of respective receptors by ligands released by gintonin treatment. ACh, acetylcholine; DA, dopamine; NE, norepinephrine; 5-HT, serotonin.