FIGURE 1.
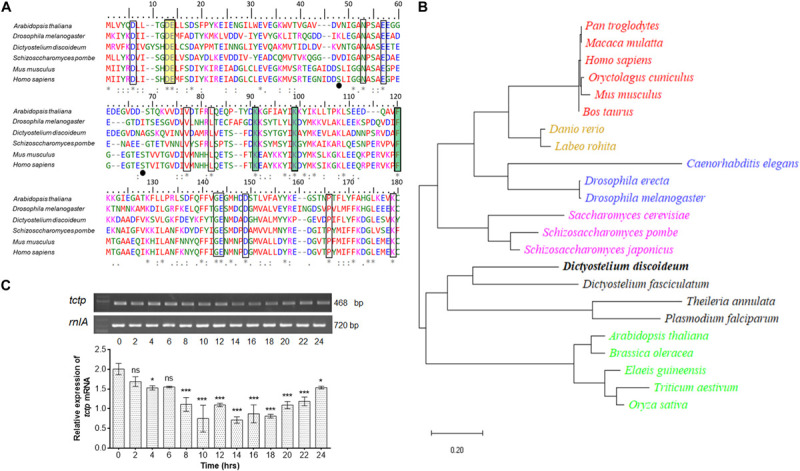
Identification and characterization of DdTCTP. (A) Protein sequence alignment of DdTCTP and other species. Sequences used in this study are: Dictyostelium discoideum (DDB0305046), Arabidopsis thaliana (Uniprot id: P31265), Drosophila melanogaster (Uniprot id: Q9VGS2), Schizosaccharomyces pombe (Uniprot id: Q10344), Mus musculus (Uniprot id: P63028), and Homo sapiens (Uniprot id: P13693). Identical [*], 90% conserved [:], and 50% conserved [.] amino acid residues are indicated in multiple sequence alignment. Residues highlighted (rectangular boxes) in different color involve in different functions which are conserved from lower to higher organisms. Residues crucial for Rheb interaction are shown in yellow color, while residues involved in microtubules and Ca2+ are highlighted in green color. Serine residues (Ser46 and Ser64) in mouse and human are known to be phosphorylated by the Plk (Polo like kinase) marked in black dots, are only conserved in mammalians. (B) Phylogenetic analysis of various TCTPs from protozoa and other species. Evolutionary distances between sequences are indicated as given scale in bottom. (C) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR of tctp transcript at different developmental time points. The values represent mean ± standard deviation; n = 3; ***p < 0.001, *p < 0.05.
