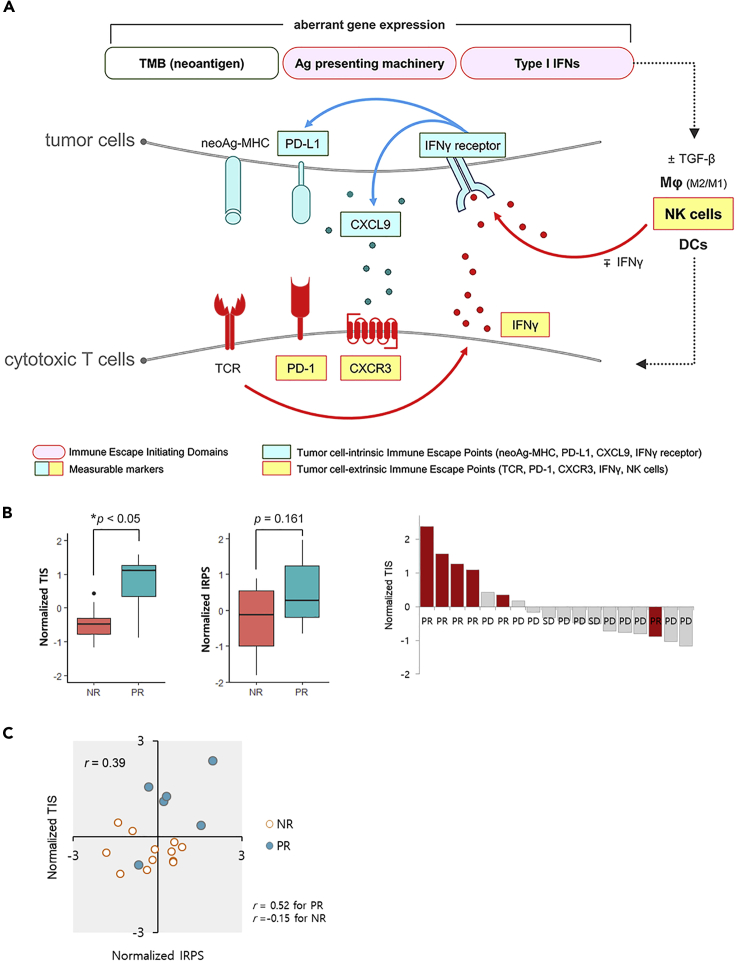
Figure 5.
Schematic Model for Major Immune Escape-Initiating Domains and Immune Escape Points in Tumor-T Cell Interaction
(A) Major immune escape points depicted in schematic model, highlighting tumor-T cell interaction at last stage of cancer-immunity cycle. Briefly, tumor cells express neoantigen as neoantigenic peptide-MHC and IFNγ receptor via antigen-presenting machinery (APM) and type I IFN (IFN1) pathway, respectively. Further, TGF-β levels in the tumor microenvironment determine macrophage polarization. Concurrently, activated macrophages (M1 type) in the proximity of tumor cells activate IFNγ-secreting NK cells, leading to IFNγ receptor activation on tumor cells. In response, tumor cells stimulate PD-L1 expression and CXCL9 chemokine secretion. The activated NK cells enrich mature DCs, which migrate to lymph nodes, activating and proliferating T cells with surface PD-1, CXCR3, and neoantigen-specific T cell receptors. The activated T cells migrate through the vascular system, extravasate, and infiltrate into the tumor microenvironment for tumor-T cell interaction. When neoantigenic peptide-MHC-TCR binding occurs, T cells secrete IFNγ and initiate tumor killing. However, when macrophages remain inactivate (M2 type), and NK cells are not activated, tumor-T cell interaction does not occur. Thus, appropriate immune responses (such as T cell-mediated tumor killing) require at least nine activated molecules in the cancer-immunity cycle, which only occurs with properly functioning APM and IFN1 pathways in neoantigen-containing tumor cells. Functional alterations in the APM and/or IFN1 pathway (i.e., immune escape initiating domains) result in immune evasion. Therefore, these nine molecules are regarded as major immune escape points (7 points in the boxes are measurable). (B) To obtain the evidence for an important role of immune escape initiating domains in determining the immune response, Gene Expression Omnibus database GSE93157 was used as an independent cohort. Normalized TICs or IRPs for patients within the cohort were plotted against ICB responses. ∗p<0.05, Student's t test. (C) For another line of evidence, the normalized TICs were plotted against the normalized IRPs. NR: no response; PR: partial response; PD: progressive disease.