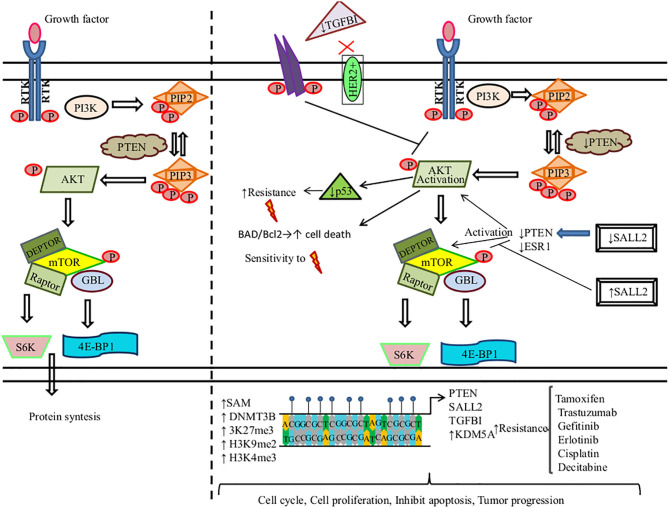
Figure 2.
DNA methylation regulates the PI3K/PTEN/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in the resistance to therapy in cancer. (Left) PI3K induces the phosphorylation and activation of AKT/mTOR. This transduction signal begins with the activation of the membrane tyrosine kinase receptors (RTKs) or G-protein-coupled receptors, which promotes the change of phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate (PIP2) in phosphatidylinositol (3-5)-trisphosphate (PIP3). The activation of PI3K (phosphoinositide-3-kinase) is regulated by the phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) by dephosphorylating PIP3 into PIP2. (Right) We show the aberrant methylation of the PTEN, Spalt-like transcription factor 2 (SALL2), transforming growth factor beta-induced protein (TGFB1), and Lysine (K)-specific demethylase 5A (KDM5A) genes through the high expression of methyltransferase (DNMT3B), s-adenosylmethionine (SAM), H3K27me3, H3K9me2, and H3K4me3, promoting a continued activation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway associated with resistance therapy in solid tumors.  , phosphorylation; ↑, increase; ↓, decrease;
, phosphorylation; ↑, increase; ↓, decrease;  , methylation,
, methylation,  , radiotherapy.
, radiotherapy.