Figure 1.
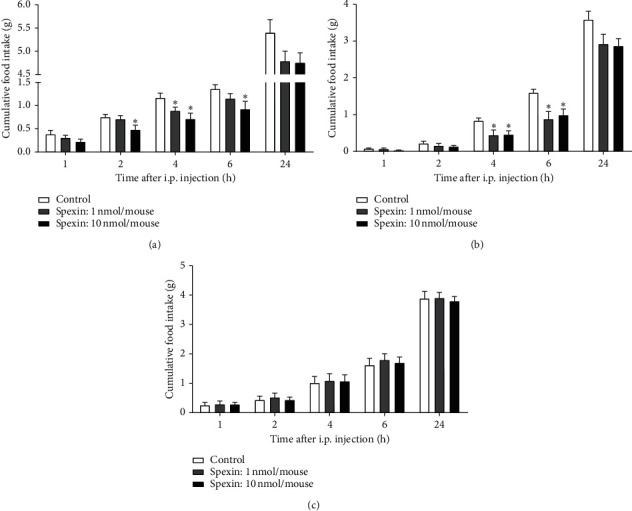
The effect of peripheral injection of spexin (1 and 10 nmol/mouse, i.p.) on food intake in mice (a). The effect of spexin on cumulated food intake in fasted mice during the light period. Spexin or normal saline (NS, control) was injected at the onset of the light cycle (b). The effect of spexin on cumulated food intake in freely feeding mice during the dark period. Spexin or NS was injected at the onset of the dark cycle (c). The effect of spexin on cumulated food intake in high-fat diet mice during the light period. Spexin or NS was injected at the onset of the light cycle. All data are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. n = 9−10 per group. ∗p < 0.05 versus the control. One way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's post hoc comparisons was performed.
