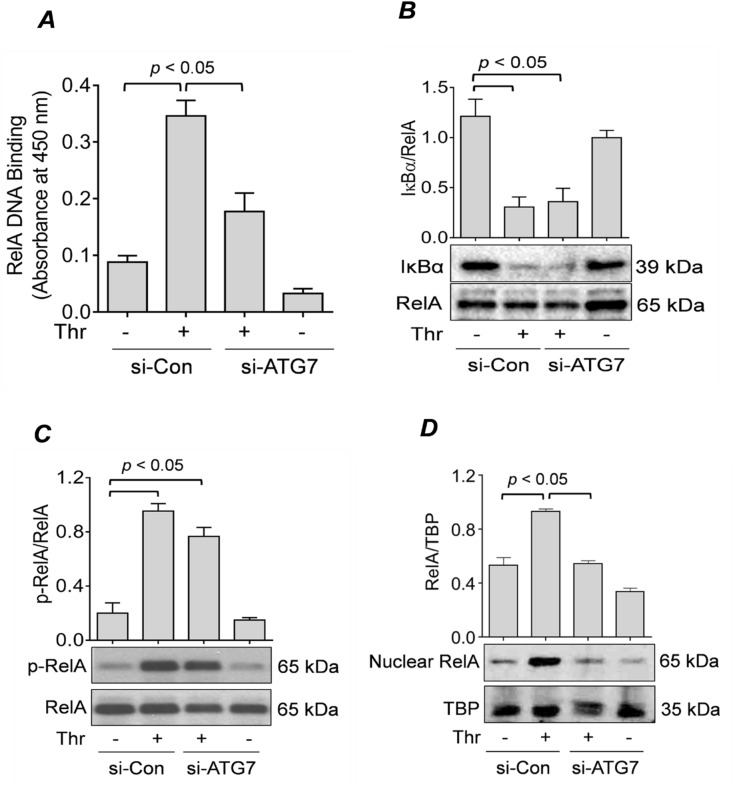
Figure 3 .
ATG7 knockdown prevents RelA/p65 nuclear translocation and DNA binding, but not IκBα degradation or RelA/p65 phosphorylation. (A) HPAEC were transfected for 48 h with si-Con or si-ATG7 and then treated with thrombin (5 U/ml) for 1 h. Nuclear extracts were obtained and processed according to an ELISA-based DNA binding assay kit as described in the “Materials and Methods” section. Error bars represent mean ± S.E. (n = 4 for each condition). (B&C) HPAEC were transfected with si-Con or si-ATG7 for 48 h and treated with thrombin (5 U/ml) for 1 h. Total cell lysates were analyzed by Western blot for (B) IκBα levels and (C) RelA/p65 phosphorylation. RelA/p65 was used as a loading control. Error bars represent mean ± S.E. (n = 3–4 for each condition). (D) HPAEC were transfected for 48 h with si-Con or si-ATG7 and treated with thrombin (5 U/ml) for 1 h. Nuclear extracts were obtained and analyzed by Western blot to measure the level of RelA/p65, and TATA-binding protein (TBP) was used as a loading control for nuclear protein. Error bars represent mean ± S.E. (n = 3–4 for each condition).