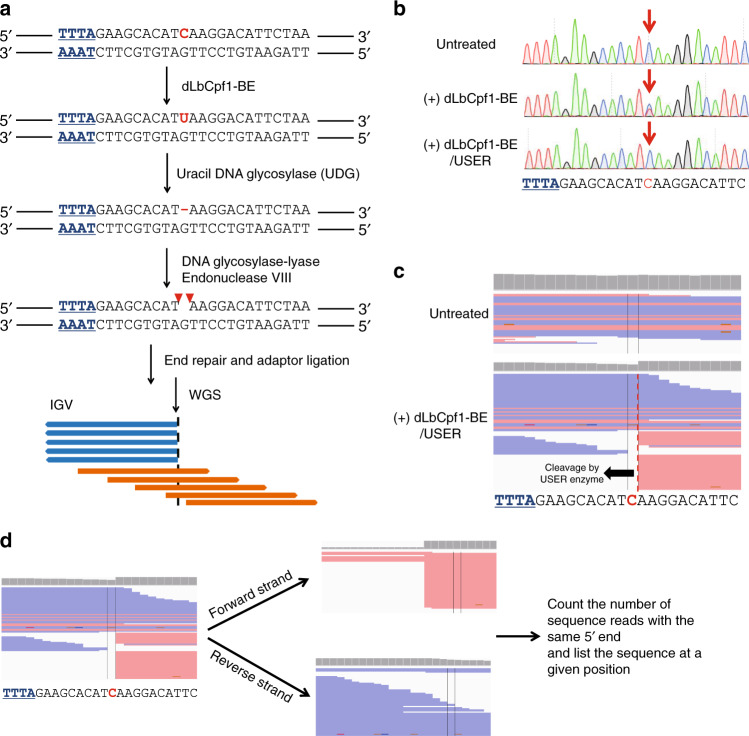
Fig. 2. Determination of the genome-wide specificity of dLbCpf1-BE using Digenome-seq.
a Overview of dLbCpf1-BE-mediated Digenome-seq. Genomic DNA is incubated with dLbCpf1-BE, which converts C-to-U within the base editing window. A single nucleotide gap is generated by treatment with USER, a mixture of UDG and DNA glycosylase-lyase Endonuclease VIII. UDG recognizes and removes a uracil base to form an abasic site, shown as a red dash. DNA glycosylase-lyase Endonuclease VIII breaks the phosphodiester backbone of the abasic site, forming a DNA SSB as indicated with the red arrowheads. The dLbCpf1-BE- and USER-treated DNA is then subjected to WGS to evaluate the genome-wide specificity of dLbCpf1-BE. b Representative Sanger sequencing results showing dLbCpf1-BE-induced C-to-U conversion and USER-induced uracil excision. The position of the sequence change is indicated by the red arrows. c IGV images showing straight and staggered alignments of sequence reads at the DYRK1A on-target site obtained using WGS. d Workflow of WGS analysis to capture genome-wide SSB sites. Sequence reads are divided into forward and reverse strands according to the read orientation. The number of sequence reads with 5′ ends at each position are then counted for each set of strands to profile off-target sites.