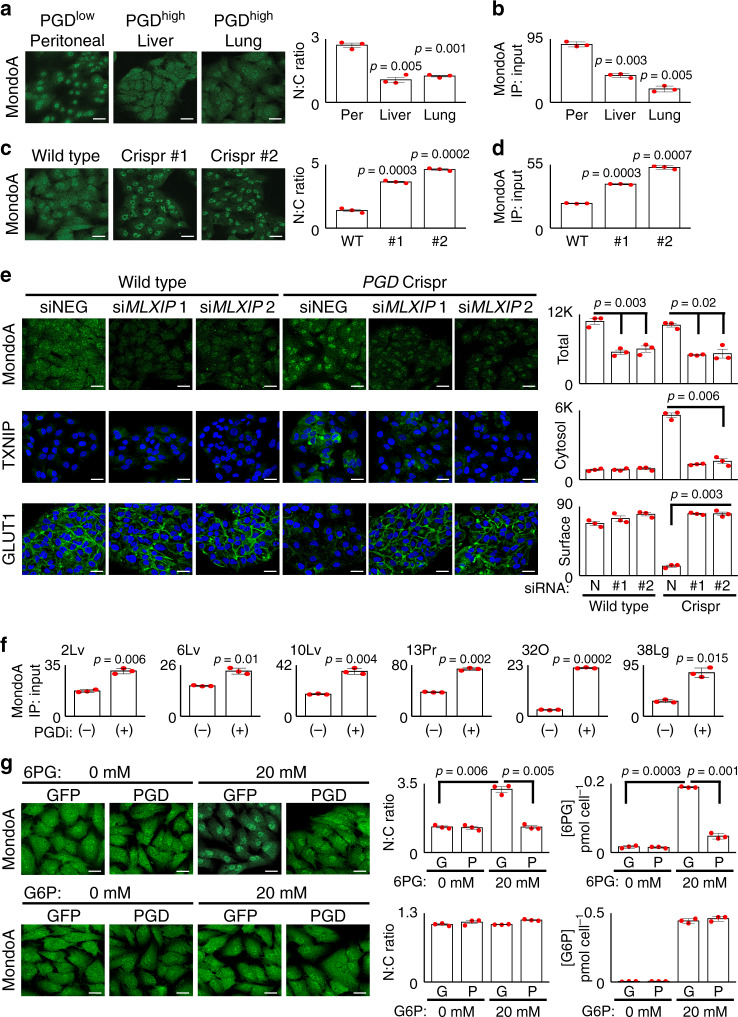
Fig. 4. PGD status influences MondoA trafficking.
a MondoA was concentrated in the nucleus of PGDlow 38Per peritoneal control cells by IF (left panel). In contrast, MondoA was distributed more equally between the nuclei and cytosol in PGDhigh liver and lung metastases from the same patient (38Lv, 38Lg). b ChIP assays also detected reduced MondoA enrichments at the TXNIP promoter in the liver and lung metastases. c PGD inactivation by Crispr/Cas (sgRNAs #1, #2) concentrated MondoA into the nucleus of PGDhigh 38Lg cells, as compared to wild-type controls. d PGD Crispr/Cas also increased MondoA enrichments at the TXNIP promoter by ChIP assays in 38Lg. e siRNAs targeting MondoA (siMLXIP #1, #2) knocked down MondoA in 38Lg cells (top panels) and prevented upregulation of TXNIP during Crispr/Cas PGD inactivation (middle panels). MondoA knockdown also rescued surface GLUT1 (bottom panels). f ChIP assays detected increased MondoA enrichments at the TXNIP promoter across the indicated PGDhigh subclones treated with PGD inhibitor (PGDi: 6AN). g (Top panels) Treatment of GFP-expressing PGDhigh 38Lg cells with excess (20 mM) 6PG concentrated MondoA in the nucleus by IF. This effect was rescued by depleting the excess 6PG with PGD overexpression4. Measurements of intracellular 6PG concentrations (right plots) confirmed that 6PG accumulated in treated GFP-expressing cells and that the excess was depleted in exogenous PGD-(over)expressing cells. Bottom panels: G6P control treatments failed to concentrate MondoA into the nucleus under any condition. For IF experiments: green, antibody signal; blue, Hoechst signal; n = 3 biological replicates, error bars: s.e.m., indicated p values calculated by two-tailed t tests, scale bars: 20 µm. For ChIP experiments: n = 3 technical replicates, error bars: s.d.m., indicated p values calculated by two-tailed t tests, results are representative of two biological replicates.