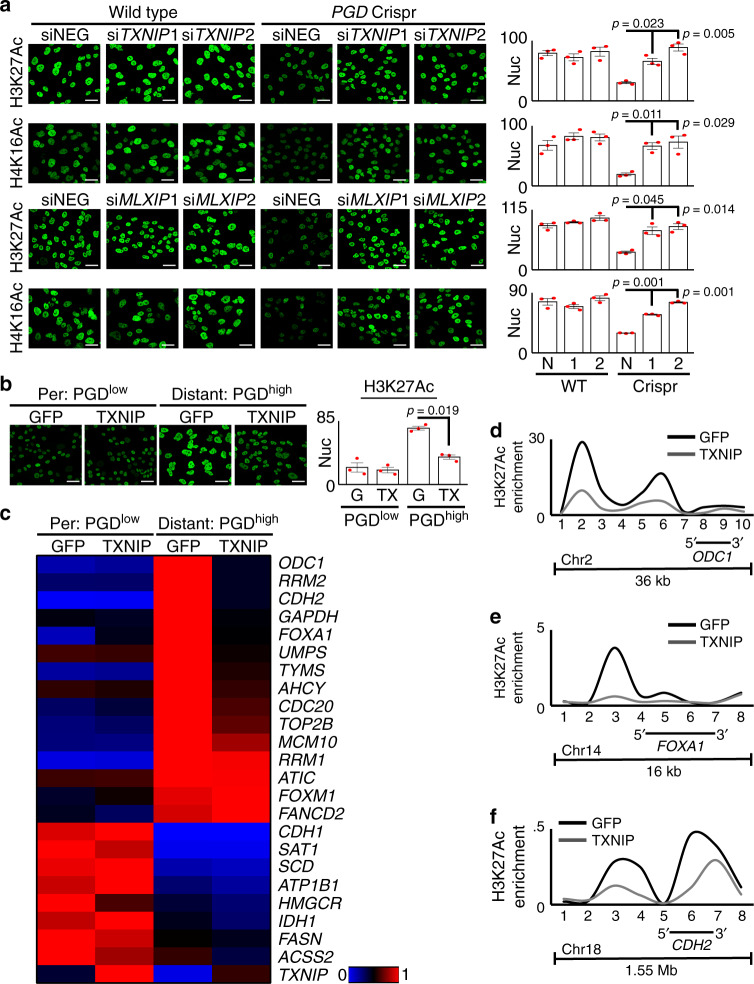
Fig. 6. PGD-driven suppression of TXNIP maintains hyperacetylated chromatin.
a RNAi knockdown of either TXNIP (top two rows: siTXNIP1, 2) or MondoA (bottom two rows: siMLXIP1, 2) rescued loss of H3K27Ac and H4K16Ac in PGDhigh 38Lg cells during PGD inactivation (right three columns: PGD Crispr). b Expression of exogenous TXNIP in PGDhigh 38Lg cells (right two panels) reduced H3K27Ac to levels comparable with PGDlow 38Per controls (left two panels). G, GFP; TX, TXNIP. c A heat map summarizing RT-qPCR data shows that recurrently upregulated genes in PDAC distant metastases (top 15, red/hot under Distant: PGDhigh GFP) were downregulated in response to exogenous TXNIP in PGDhigh 38Lg cells. A control panel of other downregulated genes (bottom, blue/cold under Distant: PGDhigh GFP) were not reactivated (n = 3 technical replicates, p values calculated by two-sided t tests are shown in Supplementary Fig. 9b and in the Source Data file). d–f Exogenous TXNIP also lowered high H3K27Ac enrichments across loci encoding ODC1 (d), FOXA1 (e), and CDH2 (f) genes in PGDhigh cells by native ChIP assays. The x-axis indicates primer locations relative to the chromosome locations depicted underneath each plot (data is representative of 2 biological replicates). For all IF experiments: green, antibody signal, n = 3 biological replicates, error bars: s.e.m., indicated p values calculated by two-tailed t tests, scale bars: 20 µm.