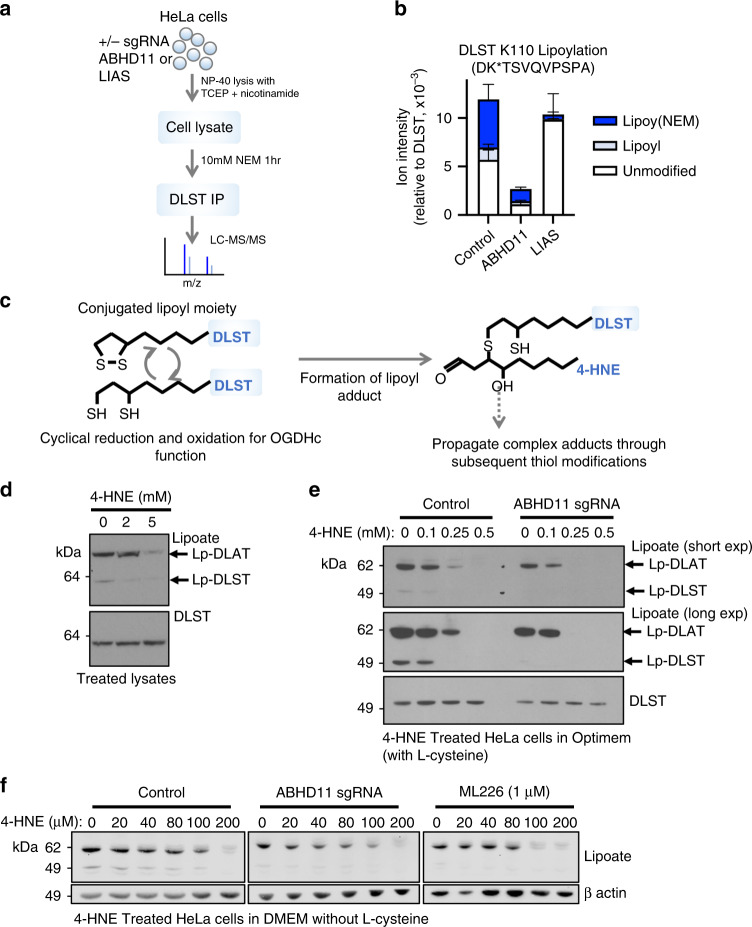
Fig. 5. ABHD11 prevents the formation of lipoyl adducts by lipid peroxidation products.
a, b Mass spectrometry analysis of DLST lipoylation. DLST was immunoprecipitated from HeLa control, ABHD11 deficient or LIAS deficient cells, and treated with NEM to modify the free thiols and maintain the lipoyl moiety in a reduced state. After SDS-PAGE, protein samples were digested with Asp-N protease and analysed by LC-MS/MS. b Normalised level of lipoylated DLST peptide compared to DLST reference peptide. Relative levels of the unmodified, NEM-dihydrolipoamide, and lipoamide DLST peptide are shown. n = 3, Mean ± SEM. c Schematic of normal cyclical reduction and oxidation of the lipoyl moiety on DLST (left). The reduced dihydrolipoamide can react with lipid peroxidation products (e.g., 4-HNE) to form lipoyl adducts through the free thiols, which may also propagate (right). d–f Effect of 4-HNE treatment on lipoylation. HeLa cells lysates were treated with 4-HNE at the indicated concentrations for 60 min (50 °C) and immunoblotted for lipoylated proteins or total DLST (d). Control or ABHD11 deficient HeLa cells were treated with 4-HNE in serum-free Optimem (e) or serum and L-cysteine free DMEM (f) for 90 min (37 °C), lysed and immunoblotted for lipoylation and total DLST. .