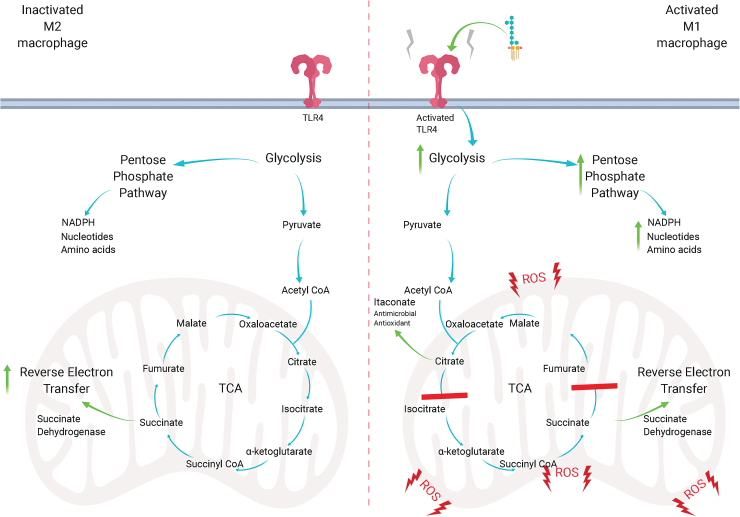
FIG. 1.
The metabolic switch. On activation by LPS, macrophages become activated, causing increases in glycolysis, which allows for rapid generation of ATP. The PPP is also upregulated, which allows for the increased generation of NADPH, nucleotides, and amino acids to assist in proliferation. The TCA cycle is broken into two parts of the cycle, after citrate, which allows the formation of the antimicrobial itaconate, and succinate, which fuels the electron transfer chain. Accumulation of succinate causes a change from oxidative phosphorylation to reverse electron transfer, increasing the leakage of electrons and generation of mitochondrial ROS. ATP, adenosine triphosphate; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; PPP, pentose phosphate pathway; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TCA, tricarboxylic acid. Color images are available online.