Figure 2.
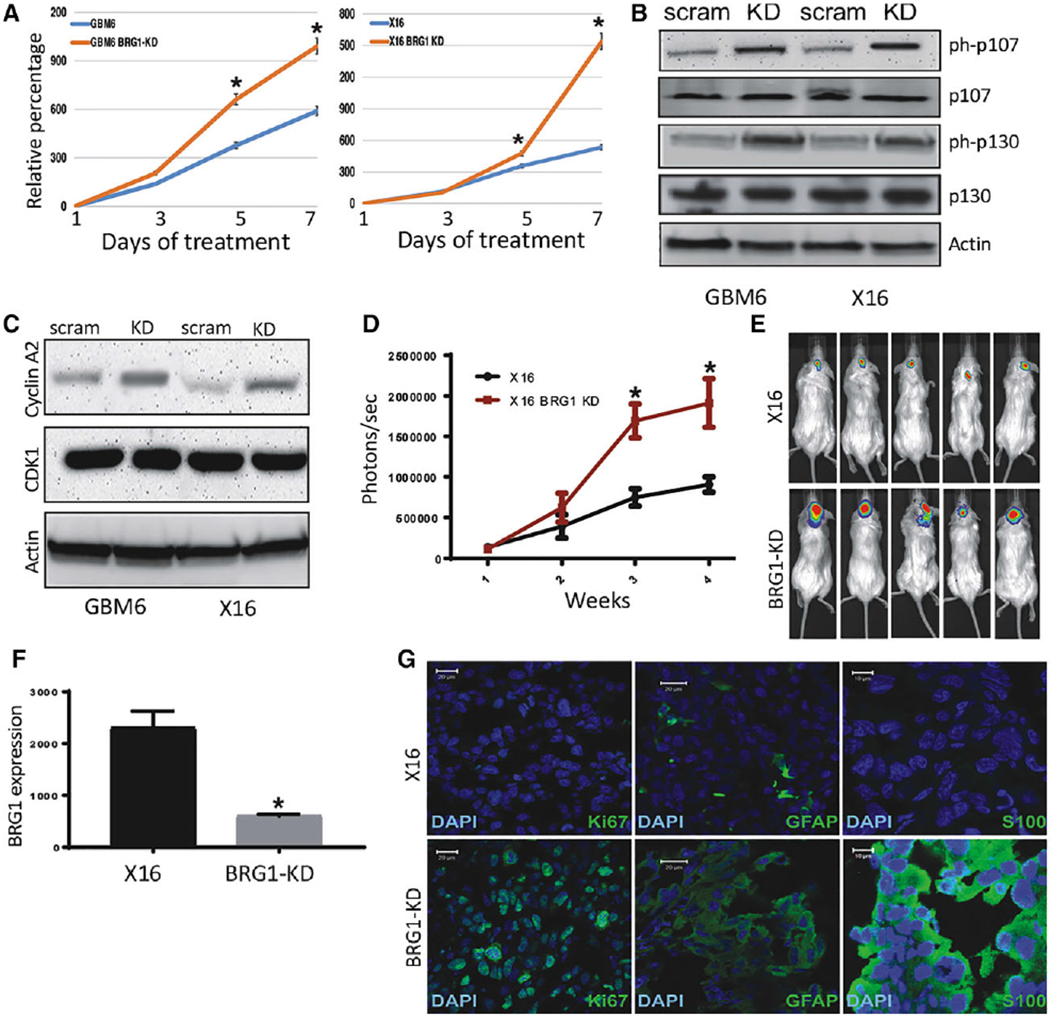
Effect of BRG1-KD on proliferation in vitro and tumorigenicity of GBM6 and X16 GICs. (A): Proliferation of BRG1-KD GBM6 and X16 GICs was determined by CellTiter-Glo assays. (B,C): Protein lysates from control and BRG1-KD X16 GICs were immunoblotted for (B) phosphorylated and total Rb protein family members, and (C) Cyclin A2 and CDK1. (D-G): Tumorigenicity was assessed by injection of 106 tumor cells into the brains of NSG mice and live animal imaging was performed at weekly intervals. (D): Quantification of the bioluminescence signal detected at 1, 2, and 3 weeks postinjection. (E): Representative bioluminescent images of mice at 21 days postinjection. (F): RNA was prepared from control and BRG1-KD X16 GIC-induced tumors and BRG1 gene expression was determined by qPCR. (G): Immunohistochemistry for GFAP, S100B, and Ki67 in X16 and X16-BRG1 KD tumor tissue. A scale bar of 20 μm is provided for reference. *p ≤ .05 was considered to be statistically significant.
