Figure 2.
A Highly Sensitive Induction Mechanism of Hippocampal Mossy Fiber PTP
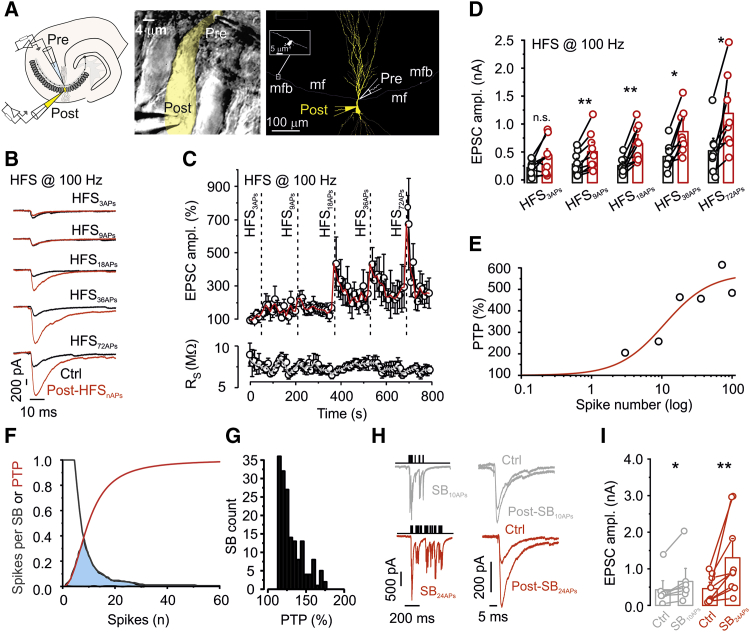
(A) Left: schematic illustration of the paired recording configuration (cell-attached recording from a presynaptic terminal, whole-cell recording from a postsynaptic CA3 pyramidal neuron). Center: representative differential interference contrast videomicrograph of a mossy fiber terminal-CA3 pyramidal neuron pair. The light-yellow area represents the 2D projection of the soma and proximal dendrite of the postsynaptic CA3 pyramidal neuron. Right: Neurolucida reconstruction of a mossy fiber terminal-CA3 pyramidal neuron pair. The mossy fiber terminal and axon are depicted in white, and the pyramidal neuron is shown in yellow. The inset shows an adjacent non-recorded terminal at higher magnification. Note that mossy fiber terminals were more than 100 μm apart; thus, transmitter release originates from the recorded presynaptic terminal.
(B) Average EPSCs before (black traces) and 20 s after (red traces) HFS with different numbers of stimuli, as indicated (HFS3APs, HFS9APs, HFS18APs, HFS36APs, and HFS72APs), all at a frequency of 100 Hz.
(C) Plot of average EPSC peak amplitude (top) and postsynaptic series resistance (bottom) against experimental time. Red and gray lines indicate running averages. Vertical dashed lines indicate time points of HFS. Data are from 9 pairs.
(D) Summary bar graph showing the effect of high-frequency stimulation with the indicated number of APs on the amplitude of unitary mossy fiber EPSCs.
(E) Plot of PTP against number of stimuli (log scale). Data points represent the mean value of PTP. Red curve, Hill function fit to the data points. Half-maximal PTP was reached with n50 = 10.8 APs.
(F) The PTP induction curve overlaps with the natural GC activity. Red curve, Hill function fit to the PTP induction data and normalized to maximum; black curve, inverted cumulative distribution of the number of APs per SB from in vivo recordings; light blue area, region of overlap between the two curves.
(G) Histogram of the predicted PTP arising from SBs with different numbers of APs measured in vivo.
(H) Left: EPSCs during an SB with 10 APs (SB10APs, top) and 24 APs (SB24APs, bottom). Right: EPSCs evoked by single stimuli before (control) and 20 s after SB10APs and SB24APs (post-SB).
(I) Summary bar graph showing the effect of SB10APs and SB24APs (9 pairs).
In (D) and (I), boxes indicate mean values, error bars denote SEM, and circles show data from individual experiments. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.