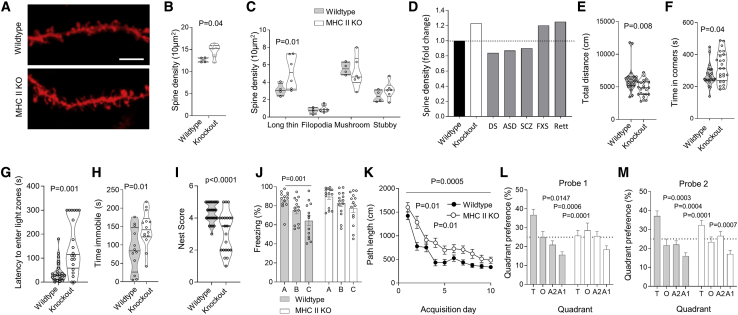
Figure 7.
Altered Neuronal Synapses and Behavior in MHC II KO
(A) Wild-type and MHC II KO mice were assessed for neuronal synapses in cortical pyramidal neurons. Representative dendritic segments; scale, 5 μm.
(B and C) Spine density in pyramidal neurons from (B) wild-type and MHC II KO mice, and (C) relative density of spine types (n = 4,6 mice, with 900–1,000 spines per condition).
(D) Comparative change in spine density in MHC II KO mice (this study) versus disease models of Down syndrome (Belichenko et al., 2007), autism spectrum disorder (Zhou et al., 2016), schizophrenia (Zhou et al., 2016), Fragile X syndrome (FXS) (Liu et al., 2011), and Rett syndrome (Jiang et al., 2013).
(E and F) Behavioral assessment of wild-type and MHC II KO mice. (E) Open field total distance moved and (F) time in the center (n = 23,24).
(G) Latency to enter light zones in light-dark test (n = 22,20).
(H) Time immobile during forced swim test (n = 12,14).
(I) Nest building scoring (n = 35,21).
(J) Contextual discrimination during generalization test (n = 13,14).
(K–M) Spatial learning in the Morris water maze. (K) Path length to finding the hidden platform (n = 24,24), (L) probe tests after 5 days and (M) 10 days (n = 21,17). Mean ± SEM.
See also Figure S7.