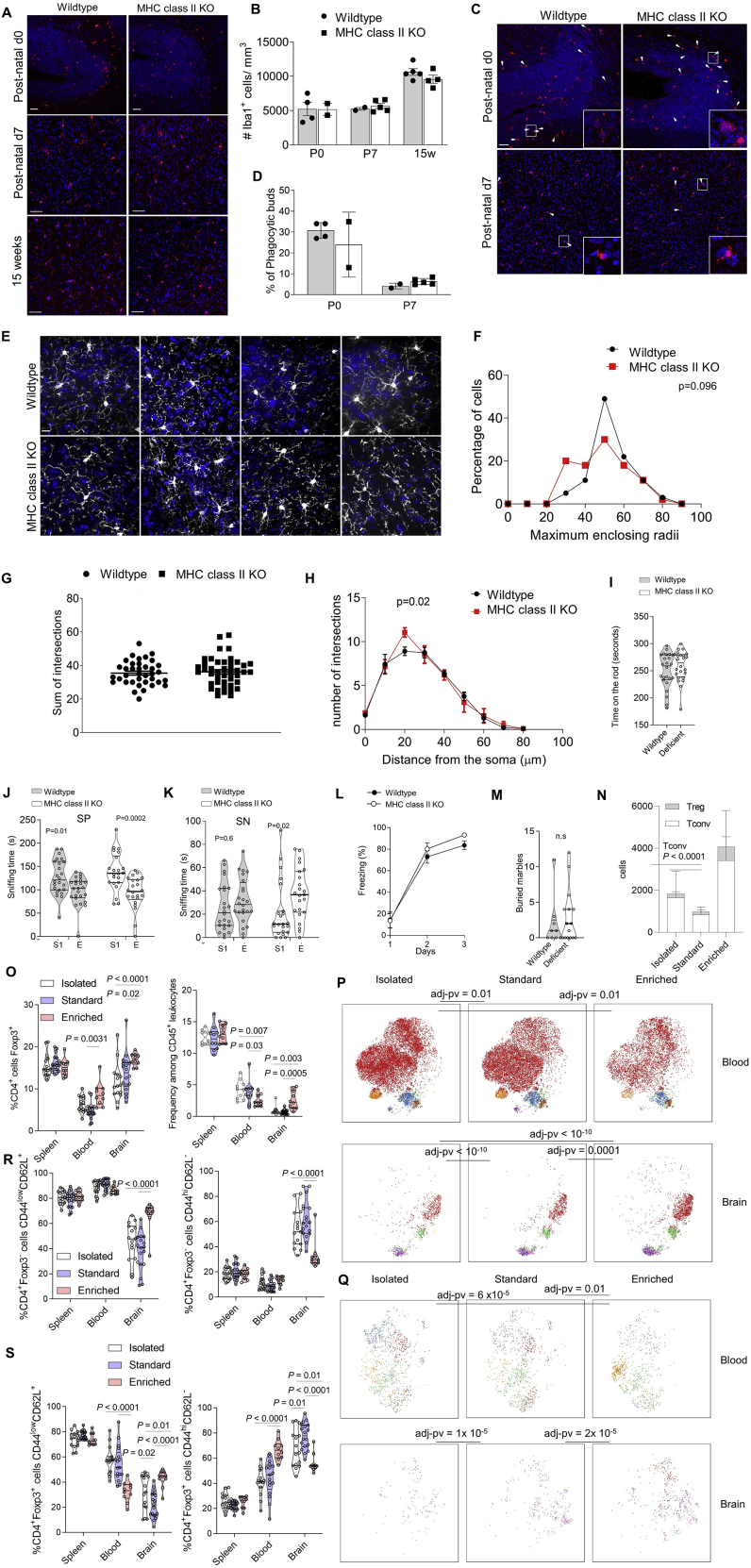
Figure S7.
Microglial Density Morphology Diverges during Development between Wild-Type and MHC II-Deficient Mice, Related to Figure 7
Microglia structure and morphology were assessed in the brain of wild-type and MHC II-deficient mice at post-natal day 0 (striatum), day 7 and 15 weeks of age. (A) Representative 20 × view of confocal images of Iba1 immunostaining showing microglial density; scale = 50μm. (B) Quantification of microglia density at post-natal day 0, day 7 and 15 weeks (n = 4,2,2,5,4,4). (C) Representative 20 × view of confocal images Iba1 labeling (red) from the post-natal day 0 (striatum) and day 7 (cortex). Scale = 50μm, arrows indicate phagocytic microglia containing engulfed DAPI+ nucleus. (D) Quantification of microglia exhibiting phagocytotic buds (n = 4,2,2,5). (E) Representative 40 × images showing microglia morphology, process extensions and ramification at 15 weeks; scale = 50μm. (F) Quantification of the proportion of microglia with a maximum enclosing radius out to varying distances. Number of microglia analyzed: wild-type = 37; MHC II-deficient mice = 44 (n = 4,4). (G) Quantification of the total number of process intersections in microglia. (H) Sholl analysis of microglia process intersections per radii (spaced with the interval of 10 μm) from the soma. Dots represent each microglia, n = 8-10 microglia/mouse (n = 4,4). Fligner-Killeen non-parametric test for difference in variance. (I) MHC II-deficient mice and wild-type siblings were assessed for behavioral abnormalities. Time spent on the rod, average of 4 repeated tests of 300 s (n = 24,25). (J) Sociability test trials to monitor the interaction with a stranger mouse (S1) compared to a empty chamber (E1) (K) and the social preference for a new stranger (S2), with interaction with repeated stranger (S1) and new stranger (S2). (n = 24,23). (L) Freezing behavior over time during context acquisition conditioning (n = 13,14). (M) Marble burying test (n = 9,14). (N) Wild-type mice were housed under standard SPF conditions, or placed under behavioral modification in the form of isolated or environmental enrichment (n = 18, 15, 10). Mice were compared by high parameter flow cytometry of the blood and perfused brain. CD4 T cells as absolute numbers of conventional cells and Tregs in the brain. P value refers to comparison of conventional T cells. (O) Proportion of Foxp3+ cells within the CD4 T cell population in blood and brain. (P) tSNE of CD4+Foxp3- T cells gated on CD4+Foxp3-CD3+CD8-CD45+ cells or (Q) CD4+Foxp3+CD3+CD8-CD45+ cells and built on CD62L, CD44, CD103, CD69, CD25, PD-1, Nrp1, ICOS, KLRG1, ST2, Ki67, Helios, T-bet, CTLA4. P values represent cross-entropy comparison to control mice. FlowSOM clusters are illustrated in color. (R) Proportion of naive (top) and activated (bottom) cells within the conventional and (S) Treg populations in the blood and brain. Mean ± SEM.