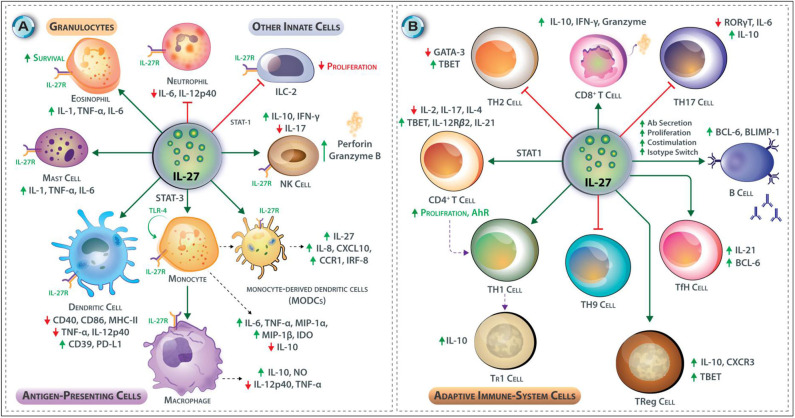
Figure 3.
(A,B) Effects of IL-27 on Innate and Adaptive immune responses. (A) IL-27 promotes cytotoxicity in NK cells through upregulation of perforin and granzyme B, and it induces IFN-γ production from NK cells via T-bet transcription factor but inhibits IL-17 production in NK cells. In mast cells and eosinophils, IL-27 promotes pro-inflammatory cytokine synthesis and release; these include IL-1, TNF-α, IL-6, promotes adhesion and survival in eosinophils. Contrary, IL-27 limits neutrophil recruitment and reduces the secretion of IL-6 and IL-12p40 from these cells. IL-27 enhances TLR4 expression by monocytes through STAT-3 and NF-κB and enhances their differentiation to macrophages. In macrophages, it induces NO expression and triggers moDCs to express IL-27, IL-8, CXCL10, CCR1 IRF8, and IFN-stimulated genes. IL-27 also induces the expression of an immunosuppressive enzyme IDO in human monocytes. IL-27 inhibits DC functions; stimulation of DCs with IL-27 before LPS reduces expression of CD40, CD86, and MHC-II but upregulation of CD39 and PD-L1. IL-27 may also inhibit the secretion of TNF-α from DCs. IL-27 inhibits the innate lymphoid cells (a subgroup of innate cells that lacks specific antigenic receptors) proliferation through STAT-1. (B) IL-27 induces T-bet and IL-12Rβ2 expression in CD4+ T cells at the early phase of T cell polarization. IL-27 inhibits the production of IL-2 by CD4+ T helper cells through induction of SOCS-3. IL-27 promotes IL-10-producing Tr1 cells. IL-27 inhibits the development of Th2 cells by downregulating GATA-3. IL-27 interferes with Th17 development by suppression of RORγt and interfering with IL-6 signaling it also stimulates IL-10 production and induction of PD-L1 on naïve T cells. IL-27 inhibits the development of Th9 cells. IL-27 supports the development of Tr1 CD4+ T cells. IL-27 also promotes the development of IL-10 secreting T-bet+ CXCR3+ Treg cells. T follicular helper (Tfh) cells produce IL-21 in the presence of IL-27. CD8+ T cells are also affected by the presence of IL-27 as it increases their proliferation and capacity to secrete IFN-γ, and granzyme B. IL-27 regulates many aspects of B cell development and their functions. In response to IL-27, B cells increase expression of Bcl-6 and Blimp1, which is critical for plasma cell differentiation.