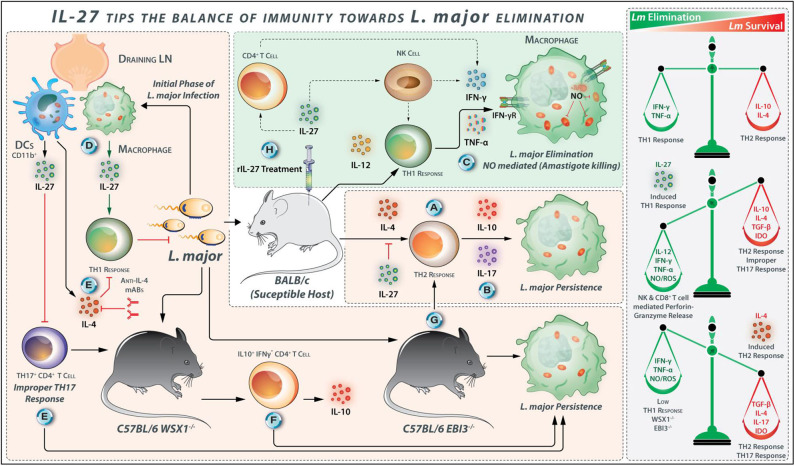
Figure 4.
IL-27 Tips the Balance of Immunity Toward L. major Elimination. (A) Promotion of L. major growth by Th2 response- IL-10 and IL-4 are identified as a factor for susceptibility in BLAB/c mice because these cytokines are drivers of Th2 type response, which promotes L. major growth. (B) Repression of IL-10 signaling increases IL-17 production and exacerbates L. major infection. (C) However, TNF-α and IFN-γ cumulatively induce iNOS expression in L. major-infected macrophages for parasite clearance. (D) IL-27 is identified as a factor that promotes resistance to L. major infection in mice. L. major-infected CD11b+ DCs are major sources of IL-27 secretion in the draining lymph nodes of C57BL/6. (E) In WSX1−/− mice, the initial immune response is accompanied by secretion of IL-4 by L. major-infected cells, and IL-4 neutralization during the early phase of infection may abolish the requirement of IL-27 for the development of an effective Th1 response. The role of IL-27 in the prevention of improper IL-17 cell development is also mentioned. (F) In WSX1−/− mice, the low percentage of IL-10+ IFN-γ− CD4+ T cells—associated with the development of more severe lesions—are found. (G) Similarly, in EBI3−/− mice, the Th1/Th2 balance is diverted toward Th2 response indicating the protective roles that IL-27 plays for immunity against L. major. (H) IL-27 stimulates CD4+ T cells and NK cells to secrete IFN-γ during the early stages of L. major infection. Therefore, exogenous delivery of IL-27 into L. major-infected BALB/c mice exhibits protection by direct suppression of Th2 response and induces protective Th1 response.