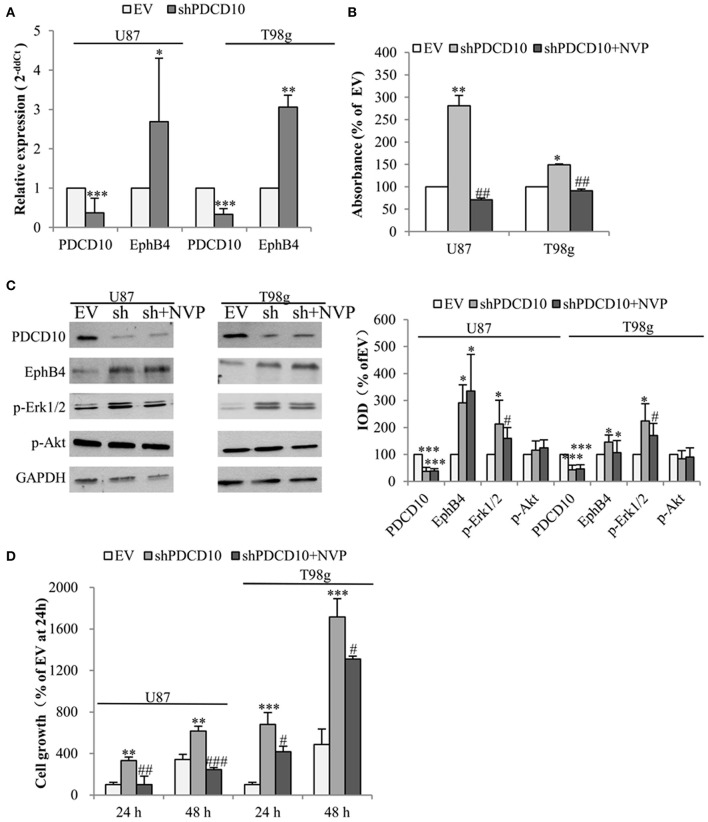
Figure 1.
Knockdown of PDCD10 increases the expression and the kinase activity of EphB4 in GBM cells and promotes cell growth, which is reversed by the treatment with the specific inhibitor of EphB4 kinase NVP. PDCD10 was knocked down in U87 or T98g cells by lentiviral shRNA transduction. (A) RT2-PCR demonstrated a significant downregulation of PDCD10 mRNA and an upregulation of EphB4 mRNA in PDCD10 knockdown (shPDCD10) U87 and T98g cells in comparison to EV-transduced cells. (B) ELISA demonstrated that knockdown of PDCD10 elevated the level of p-EphB4, reflecting the activity of EphB4, which was reversed upon the treatment with NVP (10 nM), a specific EphB4 kinase inhibitor. (C) Western blot revealed that knockdown of PDCD10 increased the EphB4 protein expression and activated Erk1/2 but not Akt in GBM cells (left). The activation of Erk1/2 mediated by PDCD10 knockdown was partially reversed by the treatment of NVP. Semiquantification of the blots was performed measuring the integrated optical density (IOD) of the blots normalized to the IOD of housekeeping protein GAPDH (right). (D) Knockdown of PDCD10 accelerated GBM cell growth. This effect was reversed by the treatment with NVP for 24 or 48 h as shown by fluorescence measurement of U87-(RFP) and T98g-(GFP) cells. For transduced U87 cells expressing RFP, the excitation wavelength was 553 nm and the emission wavelength was 574 nm. For transduced T98g cells expressing GFP, the excitation wavelength was 485 nm and the emission wavelength was 535 nm. All data presented in (A–D) were representative of at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001, compared with EV; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, compared with shPDCD10.