Fig. 5.
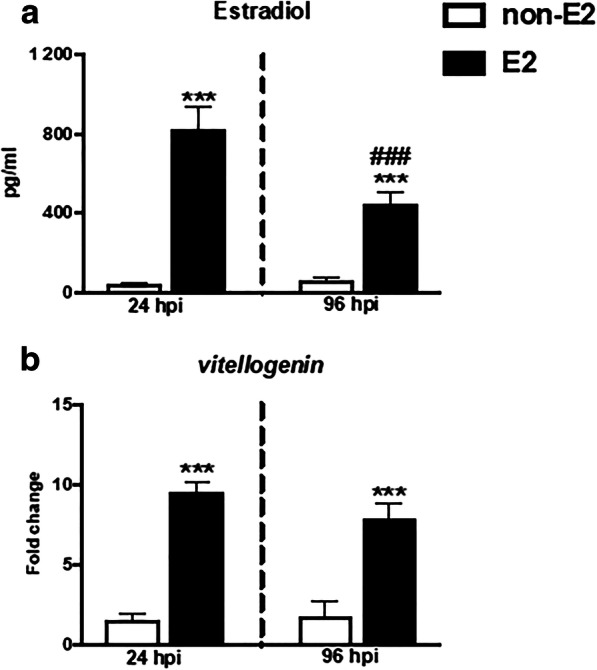
In vivo effects on the level of 17β-estradiol in blood plasma (a) and gene expression of vitellogenin in liver (b). Fish were fed for 14 days with control food (non-E2) or food treated with 17β-estradiol (E2, 20 mg/kg food). On day 14 of E2 feeding, fish were injected i.p. with A. salmonicida (4 × 108 bacteria in 250 μL PBS per fish). At 24 and 96 h post-infection (hpi), the blood (to measure E2 level) and livers (to measure vitellogenin gene expression) were collected. Averages and S.E. (n = 7). Changes in gene expression are shown as x-fold increase compared to the control group (CTR) and standardized for the housekeeping gene 40S ribosomal protein s11. Stars (*) indicate statistically significant differences between control (CTR) and E2-treated animals (***p ≤ 0.0001); number signs (#) indicate statistically significant differences between time points of infection (24 vs 96 hpi) (###p ≤ 0.0001)
