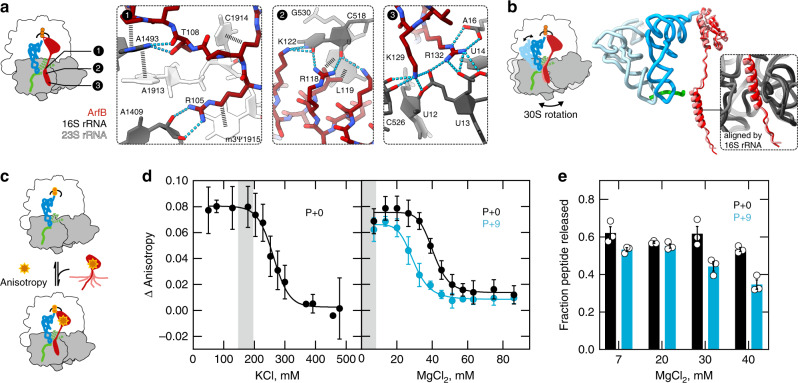
Fig. 3. Specific interactions with the ribosome stabilize ArfB in the active state.
a ArfB residues known to be essential for ribosome rescue10 form a network of interactions with the ribosome as seen in the P + 9 cryo-EM structure. Panels 1, 2, 3 depict distinct regions in ArfB indicated in the schematic (left). b Subunit rotation changes the position, but not the interactions of ArfB on the ribosome in the P + 9 hybrid state cryo-EM structure. c Experimental assay to measure the affinity of ArfB binding to stalled ribosomes using the anisotropy change of fluorescein-labeled ArfBGAQ (ArfBGAQ(Flu)). d Role of electrostatic interactions in ArfB binding to the ribosome. P + 0 or P + 9 complexes (0.15 µM) with ArfB(Flu) (0.05 µM) at different KCl (left) or MgCl2 (right) concentrations. IC50 is ~260 mM for KCl and ~40 mM for MgCl2 (P + 0) or ~30 mM for MgCl2 (P + 9). The range of physiological ion concentrations is highlighted in gray (180–200 mM for K+ and 2–3 mM for Mg2+; Ref. 23). Error bars indicate the SEM of three biological replicates, and the solid lines are dose-response fits. e Effect of Mg2+ concentration on ArfB activity. P + 0 and P + 9 complexes (0.1 µM) were incubated with ArfB (1 µM) for 5 min at 20 °C. Error bars indicate the SEM of three biological replicates.