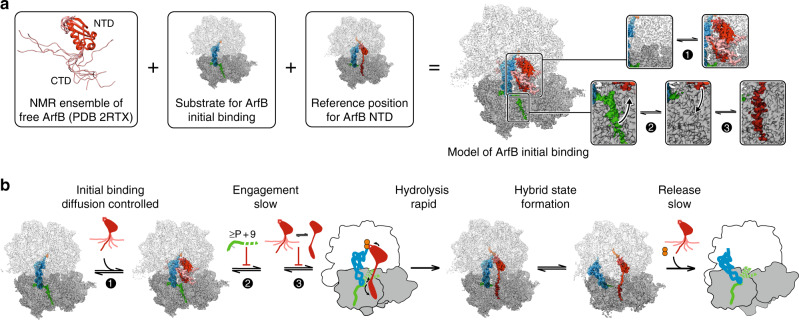
Fig. 5. Mechanism of ribosome rescue by ArfB based on rapid kinetics and cryo-EM data.
a Model for initial binding of ArfB, based on the NMR ensemble of free ArfB10 and cryo-EM structures of the P + 9 ribosome-ArfB complex. 1, 2, 3 illustrate the key steps of the mechanism. b Mechanism of ArfB action. When the ribosome stalls on a truncated mRNA, ArfB can rapidly bind regardless of the mRNA length (1). Subsequent conformational rearrangements allow the factor to probe the mRNA entry channel; if there is mRNA extending past the P site, the mRNA must first move out of the mRNA entry channel (2), a process that occurs more slowly with longer mRNAs. The binding and folding of the ArfB C-terminal domain result in the engagement of ArfB on the 30S subunit (3), which allows the rapid hydrolysis reaction to occur via the GGQ motif in the PTC, followed by peptide release, ribosome rotation and movement of the tRNA into the hybrid state, and ArfB dissociation.