Figure 2. The relation between the frequency of psychosocial stress exposure and maximal (A) and cumulative (B) norepinephrine (NE)‐induced vasoconstriction in healthy young adults (n=18; 10 women).
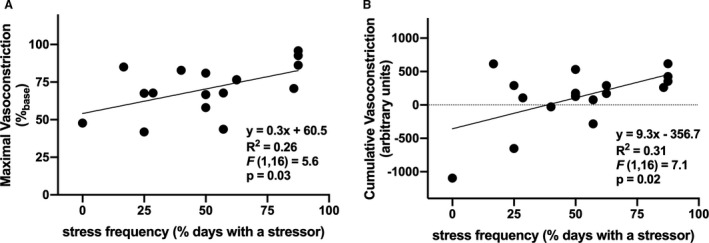
Increased psychosocial stress exposure was positively related to increased norepinephrine‐induced vasoconstriction.
