Figure 1. Ablation of Nck (noncatalytic region of tyrosine kinase) 1 and Nck2 adaptor proteins reduces shear stress–induced endothelial permeability.
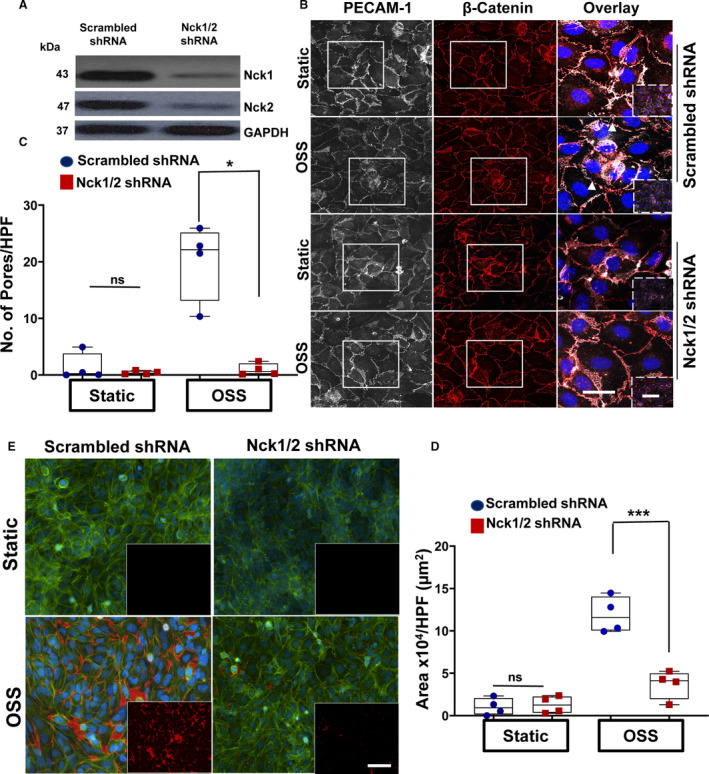
A, Representative blots showing the efficiency of the knocking down of Nck1/2 in human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs) after Nck1/2 short hairpin RNA (shRNA) or scrambled shRNA control transduction. B and C, PECAM‐1 (platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule‐1; white)/ß‐catenin (red)–stained cells showing paracellular formation after oscillatory shear stress (OSS; ±5 dynes/cm2 with 1 dyne/cm2 forward flow) exposure. Images in the boxes indicate areas of higher magnifications, whereas areas in the dashed boxes indicate lower magnifications. Data analyzed by Kruskal‐Wallis test (*P=0.03). White arrowheads indicate paracellular pores. D/E, Nck1/2 knocking down prevents flow‐induced permeability using biotinylated gelatin/Alexa 647‐streptavidin assay. 4′,6‐Diamidino‐2‐phenylindole (blue; nuclei), phalloidin (green; F‐actin fibers), and streptavidin (red; exposed biotinylated gelatin). Images analyzed using NIS‐Elements software. Scale bars=50‐100 μm. Data are from n=4 independent experiments. Data are reported using box and whisker plots and analyzed by 2‐way ANOVA and Bonferroni posttest (***P<0.001).
