Figure 1. Synthesis and in vitro characterization of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) bioadhesive hydrogel.
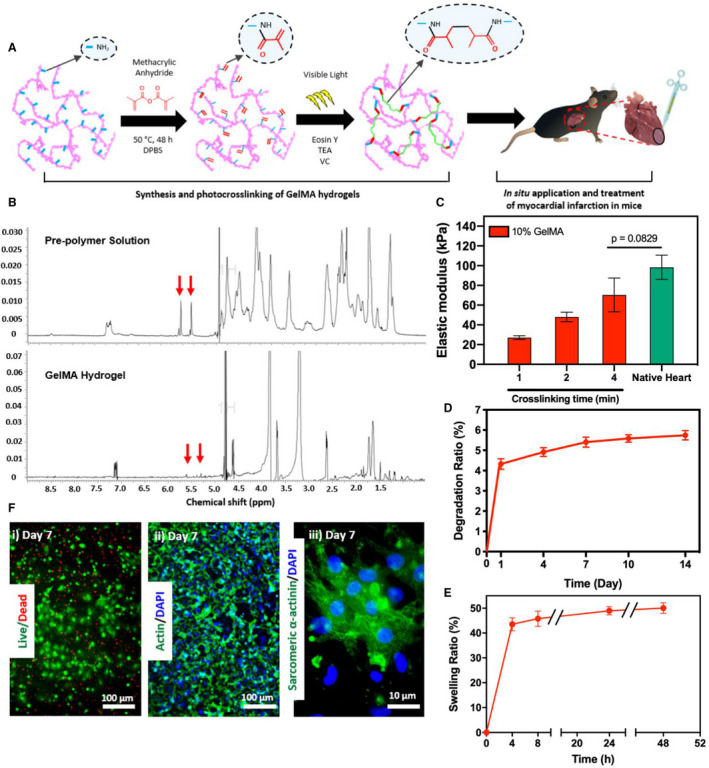
A, Schematic of the synthesis and in vitro photo–crosslinking strategy of the bioadhesive hydrogel. B, 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (500 MHz; dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)‐d6) spectra of GelMA precursor and crosslinked GelMA bioadhesive hydrogel. C, Elastic moduli of GelMA bioadhesive hydrogel produced with 10% (w/v) total polymer concentrations at different visible light exposure times, compared with native myocardium (n=4). In vitro degradation (D) and swelling ratios (E) of GelMA hydrogel (n=4). F, Representative images of (i) live/dead assay, and fluorescent staining against (ii) F‐actin/4′, 6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole (DAPI) and (iii) sarcomeric α‐actinin using 3‐dimensional (3D) encapsulated neonatal rat cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts inside the hydrogel at day 7 post‐encapsulation. Data are shown as mean±SD. P values were determined by 1‐way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's multiple comparisons test for C.
