Figure 4. ATPGD1 (carnosine synthase) attenuates aldehyde accumulation and toxicity.
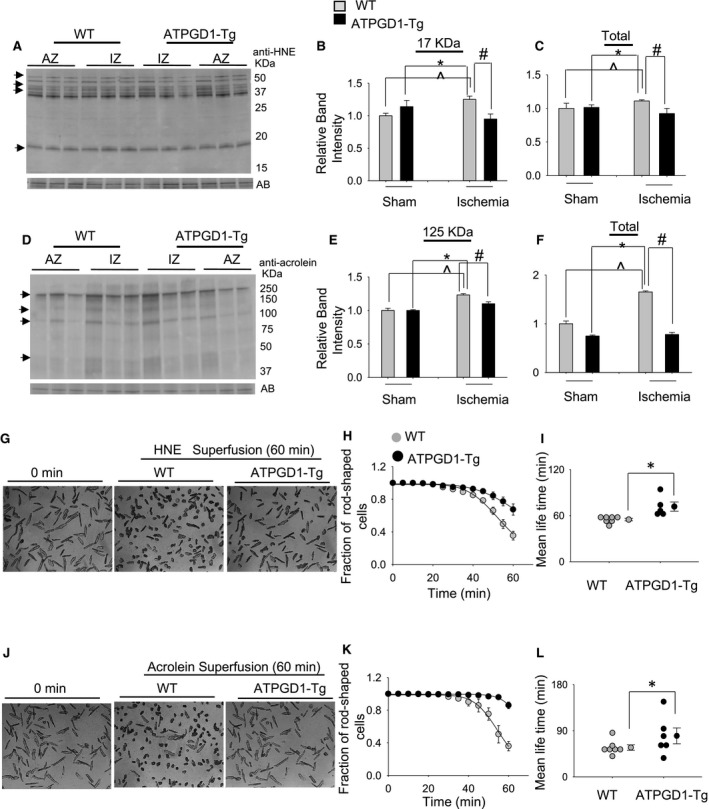
Representative Western blots of the wild‐type (WT) and ATPGD1‐transgenic (Tg) mice hearts after 30 minutes of sham and coronary ligations. The anterior zone (AZ) from sham‐operated and the ischemic zone (IZ) from coronary‐ligated mice hearts were developed with (A) anti–4‐hydroxy‐trans‐2‐nonenal (HNE) and (D) anti‐acrolein antibodies and normalized with Amido‐black (AB). Relative band intensities of HNE (B and C) and acrolein‐modified (E and F) protein bands. Data are mean±SEM. ^P<0.05 vs WT sham AZ, *P<0.05 vs ATPGD1‐Tg AZ, # P<0.05 vs WT IZ; n=4 in each group. G, Representative images of adult cardiomyocytes isolated from the WT and ATPGD1‐Tg hearts at 0 and 60 minutes of superfusion with HNE (50–60 μmol/L). (Scale bar=100 μmol/L.) H, Survival plots of cardiomyocytes isolated from WT (n=7) and ATPGD1‐Tg (n=5) hearts superfused with HNE, 100 cells from each heart. Data are shown as discrete points, and the curves are best fits of a Weibull survival function. I, Graph showing the mean lifetime of WT and ATPGD1‐Tg cardiomyocytes in the presence of HNE are presented as mean±SEM. *P<0.05 vs WT HNE superfused cardiomyocytes. J, Representative images of myocytes isolated from WT and ATPGD1‐Tg hearts at 0 and 60 minutes of superfusion with acrolein (5 μmol/L). (Scale bar=100 μmol/L.) K, Survival plots of cardiomyocytes isolated from WT (n=7) and ATPGD1‐Tg (n=6) hearts superfused with HNE, 100 cells from each heart. Data are shown as discrete points and the curves are best fits of the Weibull survival function. L, Graph showing the mean lifetime of WT and ATPGD‐Tg cardiomyocytes. *P<0.05 vs WT acrolein‐treated myocytes.
