Figure 1. Flow stratification algorithms.
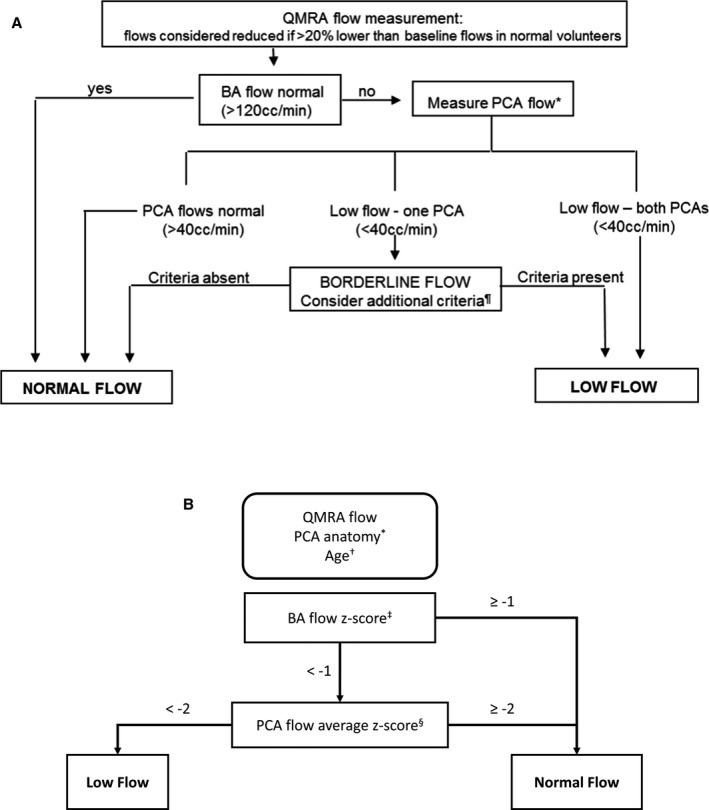
A, The original algorithm for determining a low‐flow vs normal flow state. Flow algorithm for symptomatic VB disease. *In the case of fetal PCA, determination of flow status is as follows. If 1 PCA is fetal, only the flow in nonfetal PCA is considered; if both PCAs are fetal, only flow in the BA is considered (low flow if <40 mL/min). ¶Additional criteria in borderline cases: ominous BA flow waveform oscillating ≈0, ominous symptom complex (symptoms exacerbated with head position, cannot be on anti‐coagulation/antiplatelets, requires very elevated blood pressure to avert symptoms); flow in nonoccluded proximal BA <40 mL/min. B, The optimized anatomy‐specific and age‐stratified normalizing algorithm for determining a low or normal flow state. BA indicates basilar artery; PCA, posterior cerebral artery; and QMRA, quantitative magnetic resonance angiography. *The PCA anatomy is classified as bilateral fetal PCA, unilateral fetal PCA, or no fetal PCA. †The age of patients with no fetal PCA is stratified as 18 to 60 or >60 years old. Each stratification has distinct averages and standard deviations of normal BA and PCA flows (Table 1). ‡The BA flow Z score is calculated . §The PCA flow Z score is calculated as the average of normal configuration PCA Z scores, where PCA Z scores are .
