Figure 7. Rescuing effects of vitamin K2 on Tau phosphorylation and cognitive impairment in neonatal mice from both sexes.
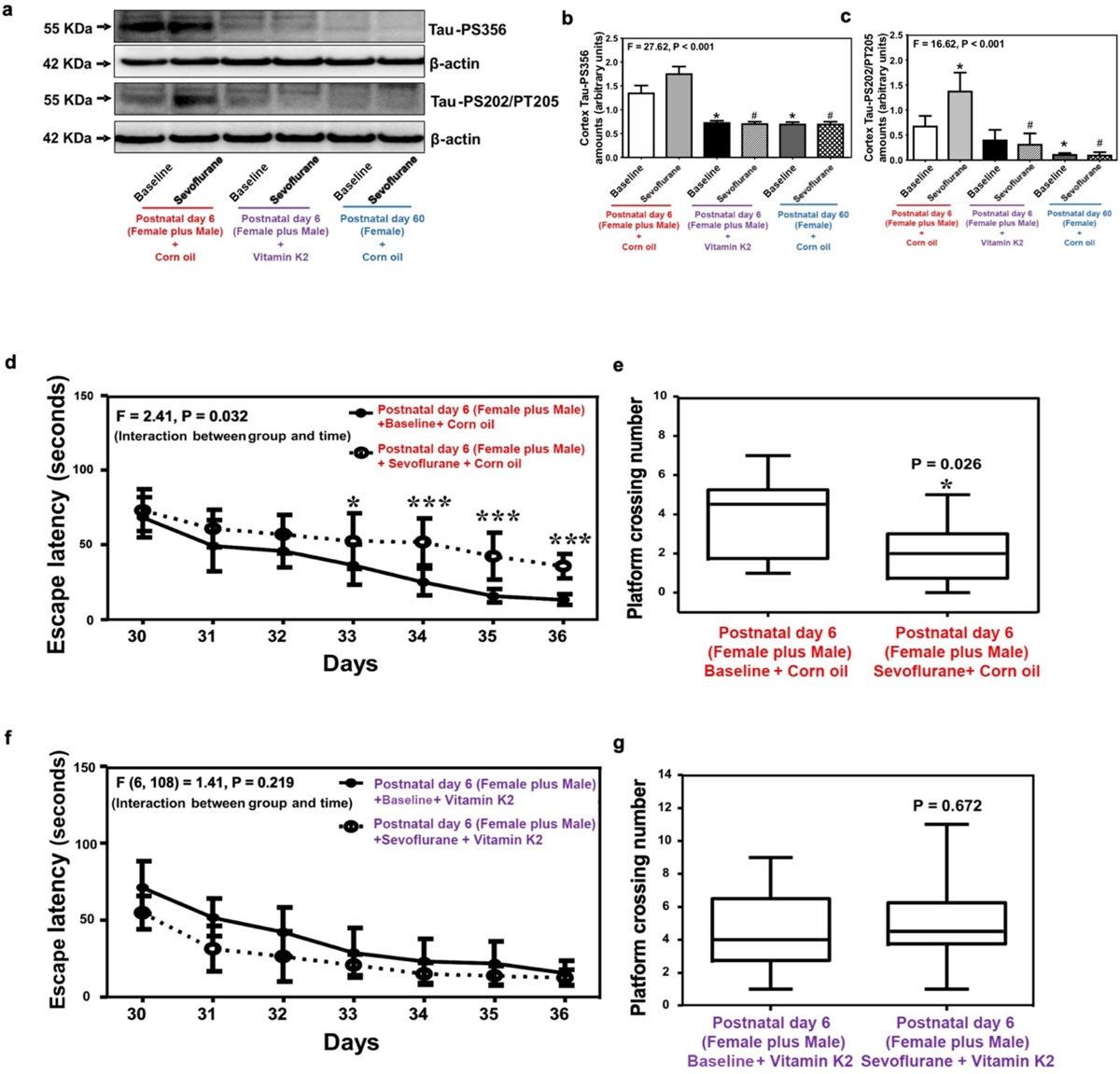
(a) Amounts of Tau-PS356 and Tau-PS202/PT205 in the cortex of neonatal mice from both sexes and female reference group mice. Summary of amounts of Tau-PS356 (b) and Tau-PS202/PT205 (c) (n=6 mice/group). Escape latency (d) and platform crossing number (e) of Morris water maze test following vehicle treatment for sevoflurane anesthesia and baseline groups (n=10 mice/group). Escape latency (f) and platform crossing number (g) of Morris water maze test following vitamin K2 treatment for sevoflurane anesthesia and baseline groups (n=10 mice/group). Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). All data are quantified and expressed as arbitrary units or real numbers compared to baseline group (non-anesthetized mice). PS, phosphorylated serine; PT, phosphorylated threonine. One-way ANOVA: (b) and (c). Two-way ANOVA with repeated measurement: (d) and (f). Mann-Whitney test: (e) and (g). *P<0.05; #P<0.05.
