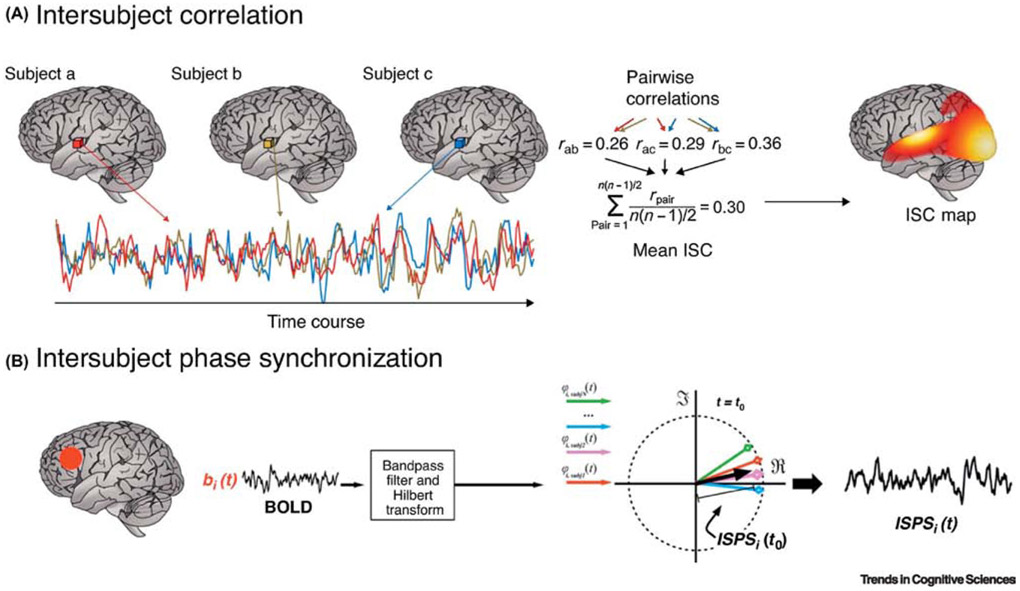
Figure 2. Analysis of inter-subject correlation of brain activity does not require a prior separation of signal and noise.
A. Inter-subject correlation (ISC) is a model-free analysis technique that requires the assumption that task-responsive brain regions will exhibit common patterns of responses (eg. changes in signal amplitude) across participants. In ISC, voxelwise time courses are correlated across all subjects, and averaged voxelwise correlations are used to create a map that represents brain areas maximally synchronized over time. B. In inter-subject phase synchronization (ISPS), a phase representation of each subject’s timeseries is created [94]. Mean voxelwise phase-based similarities are then computed across subjects and used to create an ISPS map (from [92]).