FIGURE 1.
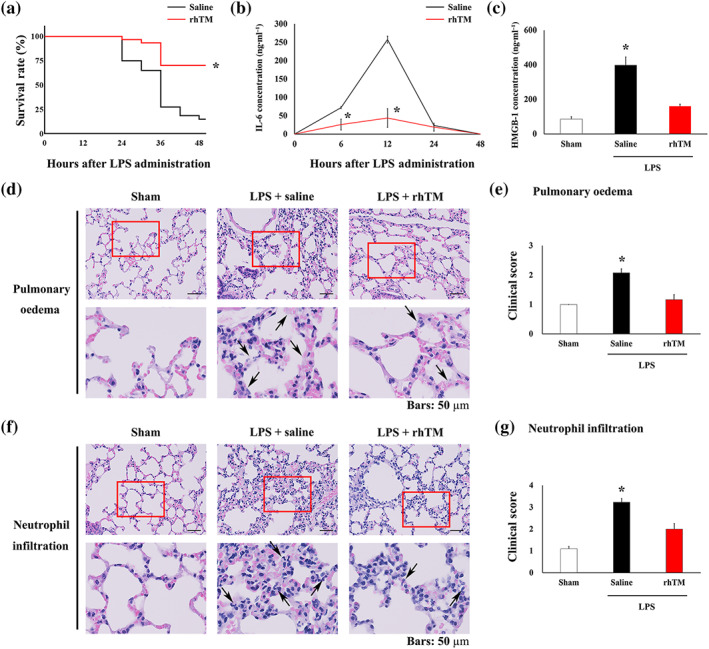
Recombinant human thrombomodulin (rhTM) treatment attenuated LPS‐induced pulmonary injury. (a) Kaplan–Meier survival curves for saline‐injected mice (n = 80) and rhTM‐treated mice (n = 30) after LPS administration. (b) Serum IL‐6 and (c) high‐mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) concentration was measured in mice using elisa (n = 6 each). (d) Haematoxylin and eosin‐stained lung tissues; arrows indicate oedema. (e) Summary data from histological scoring of lung injury caused by pulmonary oedema (n = 6 each). (f) Haematoxylin and eosin‐stained lung tissues; arrows indicate neutrophil infiltrations. (g) Summary data from histological scoring of lung injury caused by pulmonary infiltration (n = 6 each). In a and b, * P < .05, significantly different from saline‐injected mice. In c, e and g, * P < .05, significantly different from sham or LPS+rhTM
