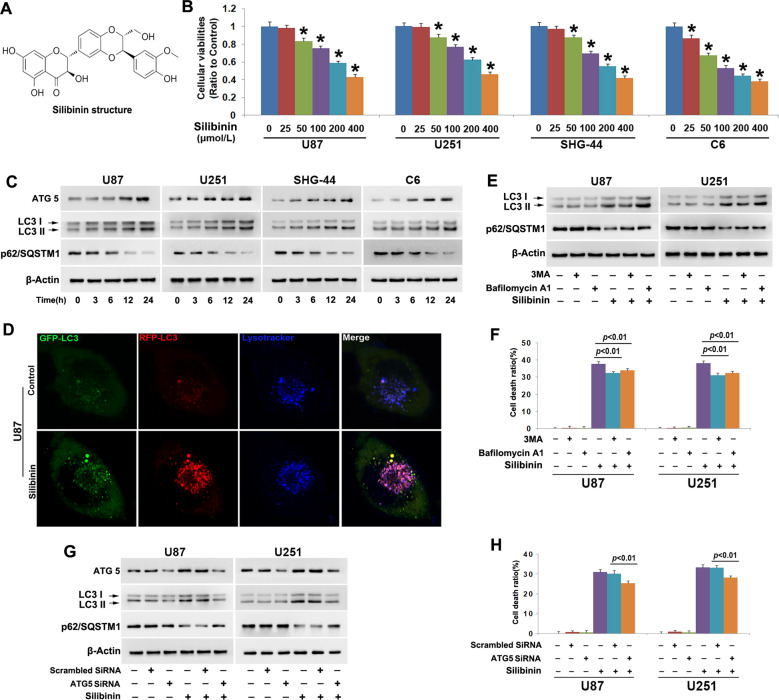
Fig. 1. Silibinin induced autophagic death in glioma cells.
a Silibinin structure. b MTT assay showed that silibinin inhibited the viabilities of U87, U251, SHG-44, and C6 glioma cells in a dosage-dependent manner. c Western blotting analysis showed that silibinin induced time-dependent upregulation of ATG5 and LC3-II, but downregulation of autophagy substrate p62(SQSTM1). d Representative images of the cells tranfected with StubRFP-SensGFP-LC3B lentivirus under confocal microscope revealed that silibinin induced formation of autophagosomes (yellow punta) and autolysosomes (violet puncta). e Western blotting analysis showed that 3MA abrogated silibinin-induced upregulation of LC3-II and reduction of p62. Bafilomycin A1 reversed silibinin-induced p62 reduction, but it further improved LC3-II levels. f LDH release assay proved that silibinin-induced glioma cell death was prevented in the presence of 3MA or bafilomycin A1. g Western blotting demonstrated that knockdown of ATG5 with SiRNA inhibited silibinin-induced upregulation of LC3-II and reduction of p62. h LDH release assay showed that silibinin-induced glioma cell death was abrogated when ATG5 was knocked down with SiRNA. The values are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 5 per group).