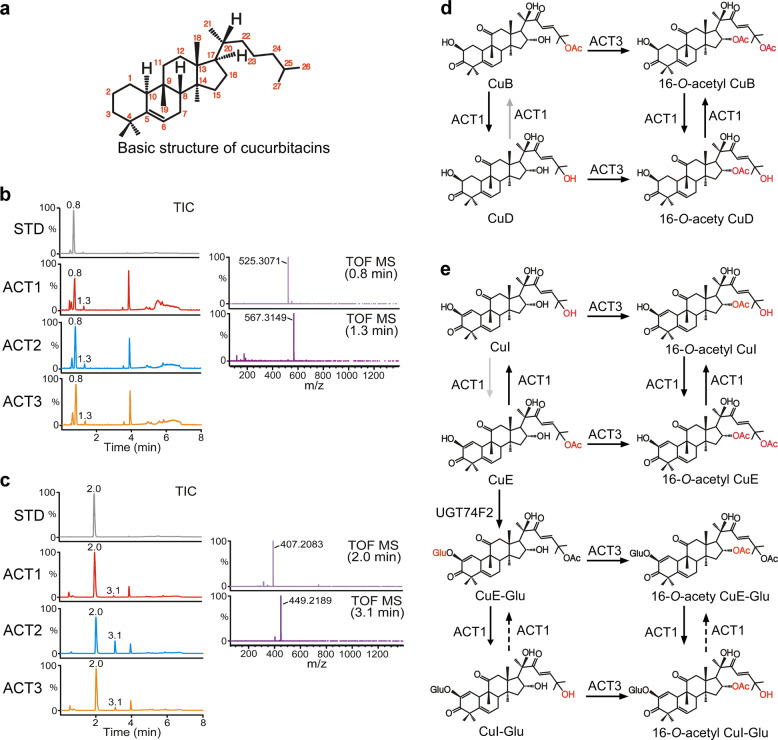
Fig. 4. Additional catalytic activity.
a Basic structure of cucurbitacins. b LC-MS analysis of extracts prepared from enzymatic reactions of ACT1, ACT2, and ACT3 in vitro using ecdysone as a substrate. The total ion chromatogram (TIC) of the ecdysone standard (STD) and reaction product in negative-ion mode shows two peaks at 0.8 and 1.3 min. Peaks in the extracted ion chromatogram at m/z 525.3071 [M+FA-H]− and 567.3149 [M+FA-H]− corresponds to ecdysone (calculated for C28H45O9 525.30639) and the ecdysone with the adducted acetyl group (calculated for C30H47O10 567.3169), respectively. c LC-MS analysis of cortisol STD and extract prepared from enzymatic reactions of ACT1, ACT2, and ACT3 in vitro using cortisol as a substrate. The TIC of the reaction product in negative-ion mode shows two peaks at 2.0 and 3.1 min. Peaks in the extracted ion chromatogram at m/z 407.2083 [M+FA-H]− and 449.2189 [M+FA-H]− correspond to cortisol (calculated for C22H30O7 407.2070) and the cortisol with the additional acetyl group (calculated for C24H33O8 449.2176), respectively. d ACT1 acetylates the C25 hydroxyl moiety of CuD and 16-O-acetyl CuD and deacetylates the C25 acetyl moiety of CuB and 16-O-acetyl CuB, producing equivalent cucurbitacins. e ACT1 acetylates the C25 moiety of CuI and 16-O-acetyl CuI and deacetylates the C25 acetyl moiety of CuE and 16-O-acetyl CuE, producing equivalent cucurbitacins. ACT1 acetylates the C25 hydroxyl moiety of CuE-Glu and 16-O-acetyl CuE-Glu, resulting in CuI-Glu and 16-O-acetyl CuI-Glu. ACT3 acetylates the C16 hydroxyl moiety of CuI, CuE, CuE-Glu, and CuI-Glu, resulting in 16-O-acetyl CuI, 16-O-acetyl CuE, 16-O-acetyl CuE-Glu, and 16-O-acetyl CuI-Glu. UGT74F2 glucosylates CuE producing CuE-Glu. Line arrows indicate the conversions identified in this study, and dashed arrows indicate the unidentified conversions. Gray arrows indicate a previously revealed conversion.