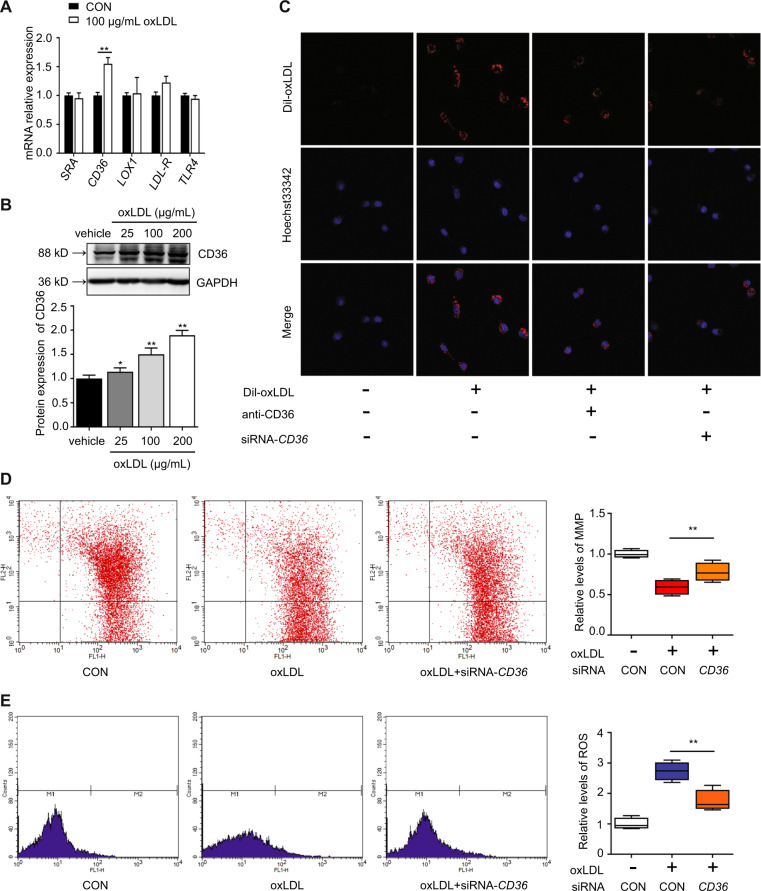
Fig. 5. oxLDL promotes lipid uptake and mitochondrial dysfunction by inducing CD36 transcription in TM3 Leydig cells.
a Cells were treated with 100 μg/mL oxLDL for 24 h, and the mRNA expression of the oxLDL-targeting scavenger receptors SRA, CD36, LOX1, LDL-R, and TLR4 was examined by qRT-PCR. b Cells were treated with various concentrations of oxLDL for 24 h, and CD36 protein expression was detected by western blotting. Quantitation of mRNA and protein expression was determined by normalization to the internal control GAPDH. No oxLDL treatment was used as a control. c Cells were preincubated with a CD36-specific antibody for 1 h or transfected with negative control (NC) or siRNA-CD36 for 24 h. Then, the cells were incubated with Dil-oxLDL for 30 min. Lipid uptake was evaluated by the fluorescence intensity of Dil-oxLDL. The cells were transfected with siRNA-CD36 or NC and then with blank control or 100 μg/mL oxLDL for 24 h. The mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) (d) and intracellular ROS (e) were assayed by flow cytometry. The data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation of at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared with the control.