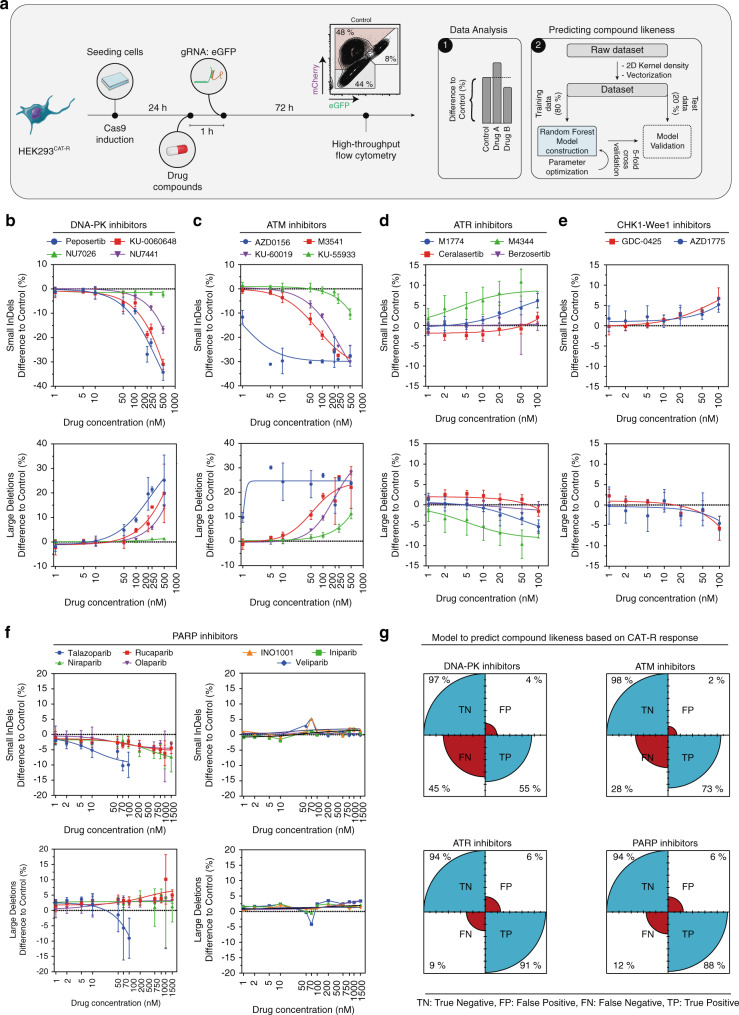
Fig. 3. A platform to screen relevant DNA damage repair inhibitors.
a The workflow of the small pharmacological compound screen. HEK293CAT-R cells induced with doxycycline (1 μg/ml) were seeded on a 96-well plate, 24 h later the cell culture medium was supplemented with the drug compounds. An hour afterwards, the synthetic gRNA: eGFP was transfected into the cells. Three days post-transfection, cells were analyzed in a high-throughput flow cytometer. Data points were averaged and normalized to the control (DMSO). Line plots (NDNA-PKi = 6, NATMi = 6, NATRi = 6, NCHK1-Wee1 = 6, NPARPi = 9, mean ± standard deviation) of flow cytometry analysis for HEK293CAT-R cells demonstrate the effect of b DNA-PKcs, c ATM, d ATR, e CHK1 & Wee1, and f PARP inhibitors on small InDels or large deletion formation. Nonlinear regression curves were calculated with the least-squares fitting method using a dose–response model. N represents the number of independent experiments. g Fourdotplot for each drug compound class. The total number of analyzed observations for HEK293CAT-R cells is 2443. To train the model a repeated cross-validation strategy is used (5-fold, 10 repeats) and an up-sampling technique to balance the compound classes. A confusion matrix is used to evaluate the performance of the test in terms of sensitivity and specificity.