Fig. 2.
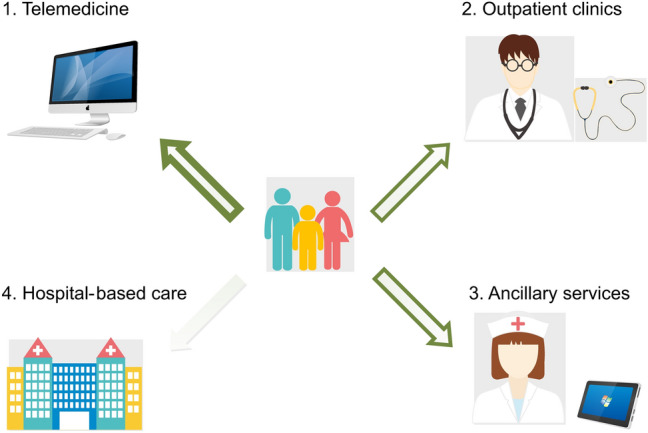
The four pillars of neuromuscular disorder centres and their function during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. This figure displays the four main organizational milestones that could improve the care of neuromuscular disorder (NMD) patients during the pandemic. The prominent use of telemedicine approaches (wide green arrow), if possible, can help to avoid unnecessary hospital visits for NMD patients. Ancillary services performed as much as possible with virtual platforms, such as pulmonary assessments, fluoroscopic swallowing studies, and neuropsychological evaluations, and outpatient clinics represent valuable alternatives to hospital visits (medium-width green arrows). NMD patients’ visits in hospital settings, particularly if dedicated to COVID patients, should be proposed more sporadically, (narrow-width green arrow), be preferred for low-risk NMD patients, and be provided following strict safety measures (see “The role of neuromuscular centre” section for more details)
