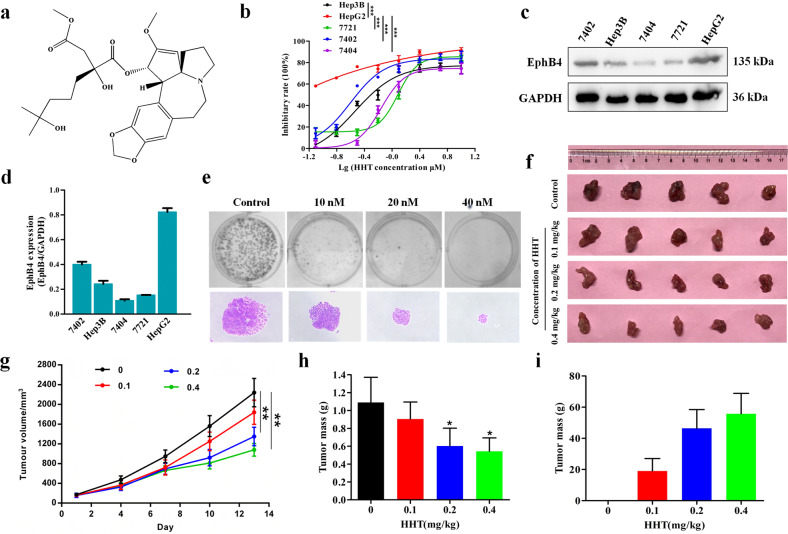
Fig. 1. HHT exhibited a growth inhibitory effect on HCC cells in vitro and in vivo.
a The chemical structure of HHT. b Effects of HHT on cell proliferation in Hep3B, HepG2, SMMC-7721 (7721), Bel-7402 (7402), and Bel-7404 (7404) cells were determined by MTT assay. ***p < 0.001 compared to the IC50 of HepG2 cells. Cells were treated with increased gradients of HHT for 48 h (n = 5 cultures for each dose). c Protein expression of EphB4 in Hep3B, HepG2, 7721, 7402, and 7404 cells. d Quantification of c (n = 3 independent experiments). e Effects of HHT on colony formation in HepG2 cells. The upper row: the colony formation picture; the lower row: the individual colony picture (×200 magnification). f Photographs of control and HHT-treated group tumors (n = 5 mice). g Tumor volume change throughout the study (n = 5 mice). h Effect of HHT on tumor inhibitory rate (n = 5 mice). g, h data represent mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; compared to vehicle controls. i Inhibitory rate of HHT on tumor mass (n = 5 mice).