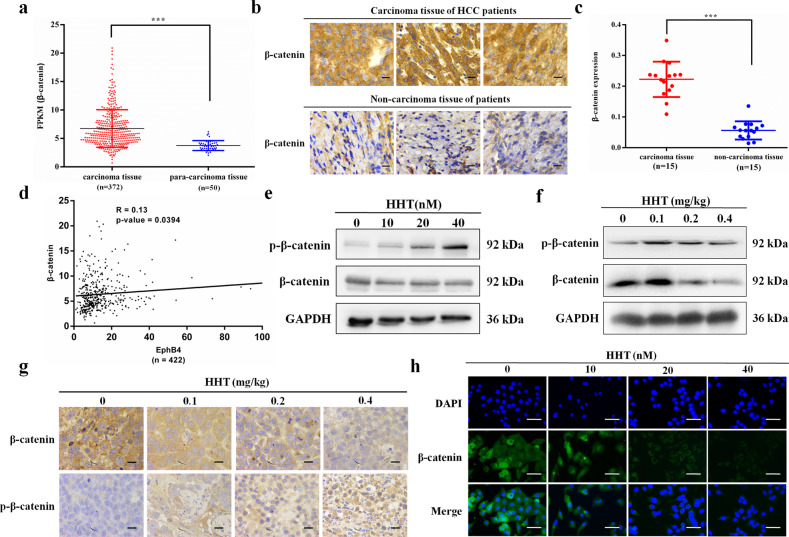
Fig. 6. EphB4 was positively correlated with β-catenin in HCC patients and HHT inhibited the phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of β-catenin.
a mRNA expression of EphB4 in HCC carcinoma tissue and para-carcinoma tissue in the TCGA database (***p < 0.001). b Representative figures of immunohistochemical analysis of β-catenin expression in carcinoma and noncarcinoma tissues derived from 15 HCC patients and 15 nonHCC patients, respectively. ×400 magnification. c Quantification of b (n = 15, ***p < 0.001). d The positive correlation between the expression of β-catenin and EphB4. e Protein expression of β-catenin and p-β-catenin in HepG2 cells treated with HHT for 48 h. f Protein expression of β-catenin and p-β-catenin in HepG2 tumor EphB4 expression after HHT treatment. g Immunochemistry assay of β-catenin and p-β-catenin in HepG2 tumor tissues. ×400 magnification. h Immunofluorescence analysis of the β-catenin protein in HepG2 cells treated with HHT. β-catenin (green), DAPI (blue) staining and merged images indicate the nuclear translocation and expression of β-catenin. Scale bars, 100 μm. All data represent mean ± SEM.