Figure 2: A. Block diagrams of the ACE2 gene and ACE2, ADAM17 and TMPRSS2 proteins.
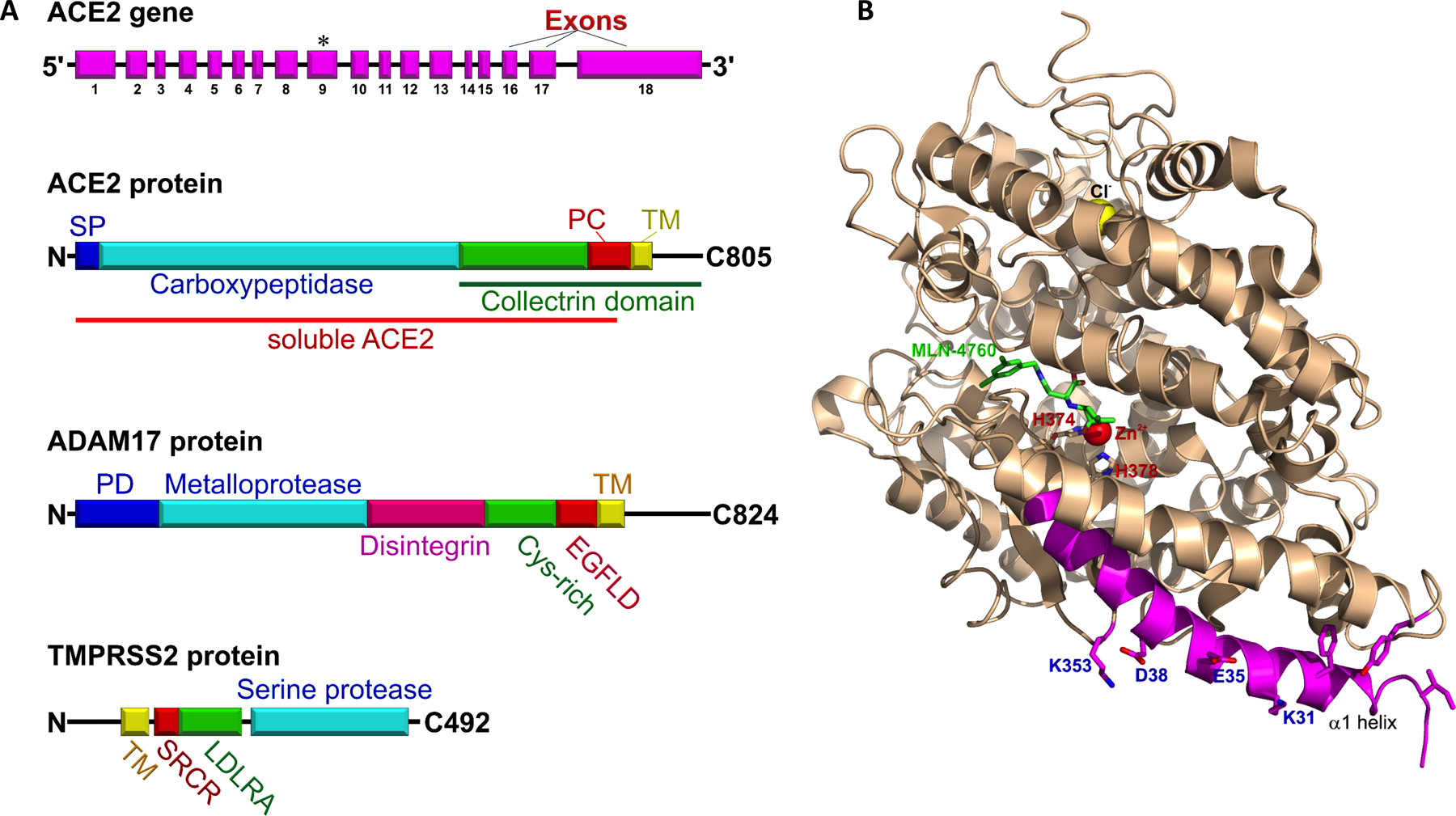
ACE2 gene, exons (magenta), asterisk indicates coding for zinc-binding site “HEMGH”. ACE2 protein comprised of N-terminal signal peptide (blue), catalytic carboxypeptidase domain (cyan), junctional segment of the collectrin domain (green), peptidase cleavage site (PC, red), transmembrane domain (TM, yellow), and the C-terminal tail. The distal part of ACE2 protein, (the protease cleavage site, the transmembrane domain and the C-terminal tail), is highly homologous to the classical collectrin domain (green line). The large proximal N-terminal ectodomain of the ACE2 protein (red line) can be shed after proteolytic cleavage by endopeptidases, such as ADAM17 and TMPRSS2. This shed segment of ACE2 is named soluble ACE2 (sACE2). sACE2 is a catalytically active serum protein. ADAM17 protein consists of the N-terminal prodomain (PD, blue), metalloprotease (cyan), disintegrin (magenta), cys-rich (green), epidermal growth factor-like (red), and transmembrane domains (yellow), and cytoplasmic tail. TMPRSS2 is a relatively short 492 amino acid protein that consists of a cytoplasmic N-terminal tail, transmembrane (yellow) and scavenger receptor cysteine-rich domains (SRCR, red), a low-density lipoprotein receptor A (LDLRA, green), and C-terminal serine protease domain (cyan).
B. A structure of human soluble ACE2 with its inhibitor (S,S)-2-[1-Carboxy-2-[3-(3,5-Dichloro-Benzyl)-3h-Imidazol-4-Yl]-Ethylamino]-4-Methyl-Pentanoic Acid (MLN-4760) at the presumed location of angiotensin I and angiotensin II catalytic site (pdb:1R4L). The cofactors Zn2+ and Cl− are shown as spheres (red and yellow, respectively). Histidine residues of the peptidase zinc-binding site HEMGH are labeled red (H374 and H378). The SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 binding site is colored magenta, with key residues for binding S1-receptor binding domain of SARS-CoV-2 blue (K353, D38, E38, and K31).
