Figure 1.
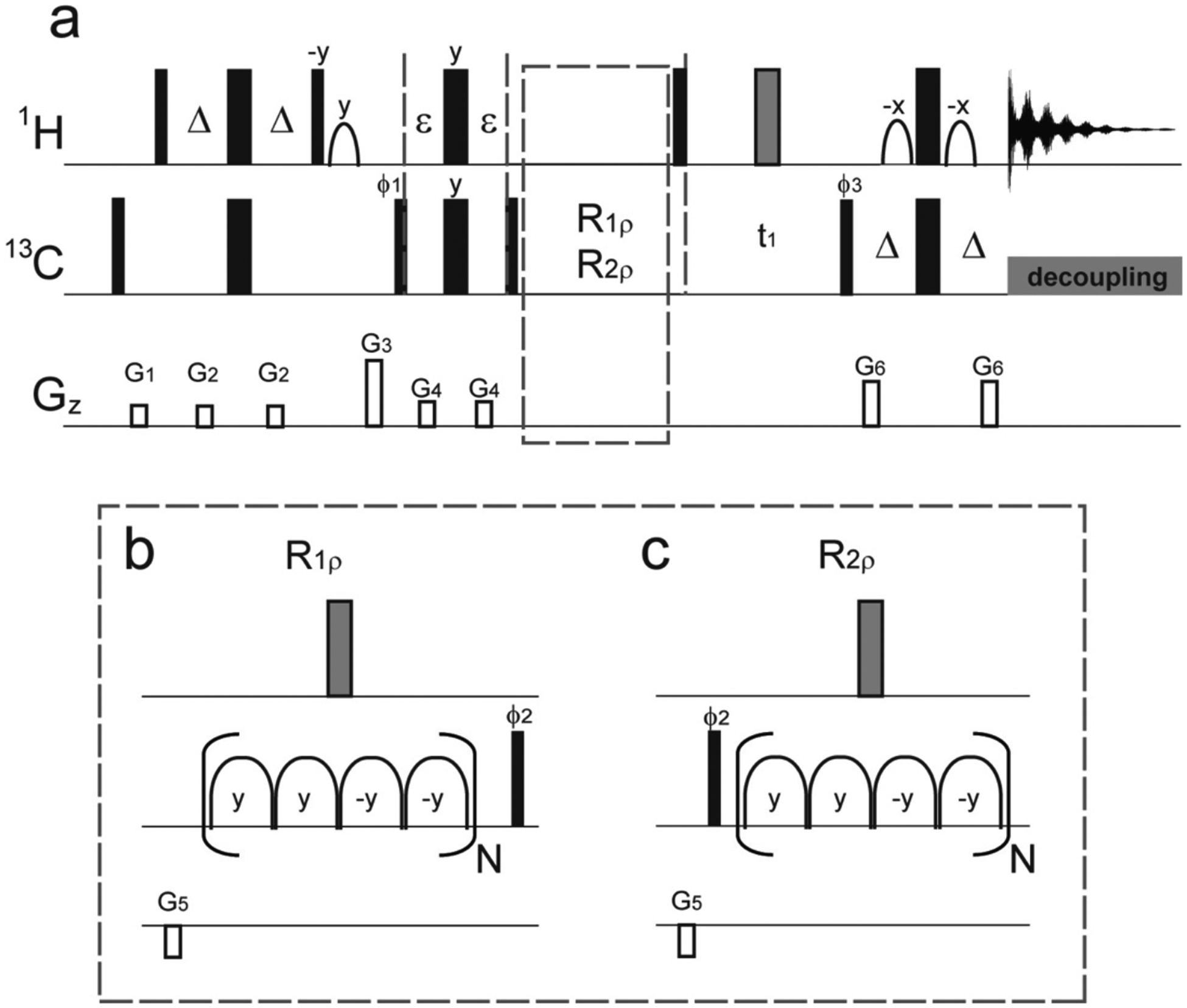
(a) Pulse sequences for the improved version of methyl adiabatic relaxation dispersion experiments. As described previously, adiabatic hyperbolic secant pulses (HSn) are used for the 13C spin-lock periods. R1ρ (or R1) relaxation delays (b) and R2ρ (or R2) relaxation delays (c) are followed after the filter element with ε = 0.6666 ms. All 90° (180°) pulses are indicated by narrow (wide) rectangles and are applied along the x axis, unless indicated otherwise. The shape pulses on the proton channel are for water flip-back and Watergate, and the gray wide rectangles are composite pulses, 90x-270y-90x. Four adiabatic pulses (b and c) are concatenated in a MLEV-4 fashion (y, y, −y, −y), and each spin-lock unit is represented by a composite adiabatic pulse (16 ms) in parentheses for both R1ρ and R2ρ experiments. Δ is set to 1.8 ms. Phases are ϕ1 = x, −x; ϕ2 = x, x, −x, −x; ϕ3 = x; and ϕrec = x, −x, −x, x. Quadrature detection in the t1 dimension is achieved by shifting the phase of ϕ3 by 90° in the states-TPPI manner. Gradient magnitudes for G1–G6 in units of (ms, G/cm) are (1, 10), (0.5, 6), (1, 50), (0.2, 10), (1, −20), and (0.5, 25), respectively.
