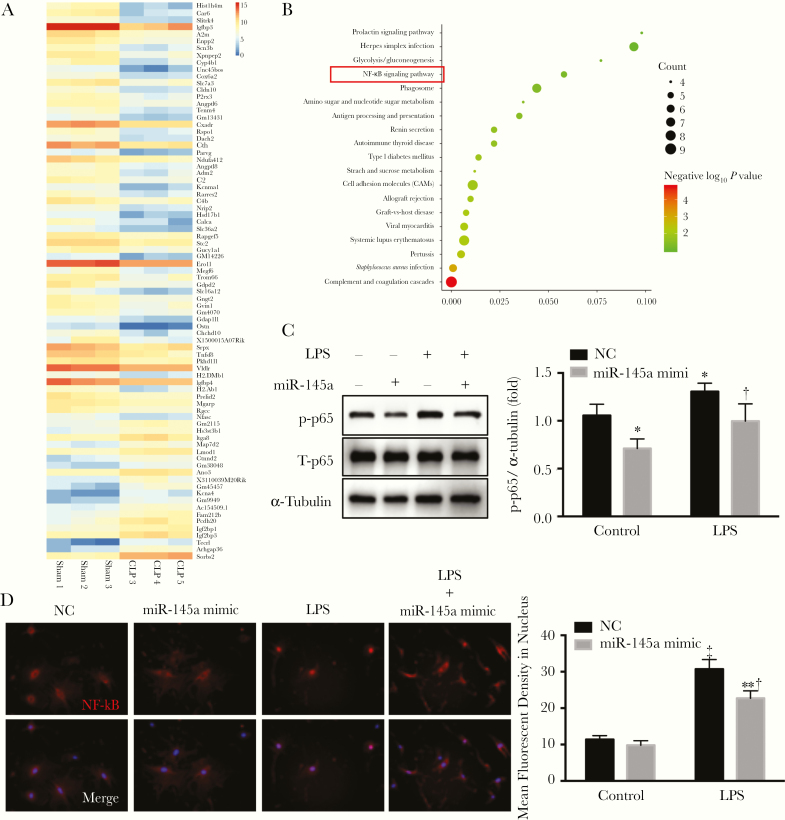
Figure 4.
miR-145a suppressed lipopolysaccharide (LPS)–induced nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) activation. A, RNA sequence data were analyzed by means of bioinformatics. B, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis was used to determine the different signaling pathways. C, D, Lung pericytes were transfected with miR-145a-5p mimic and negative control. Pericytes were stimulated with LPS (100 ng/mL) for 2 hours. C, LPS-induced NF-κB phosphorylation was determined using Western blot analysis (n = 3). *P < .05 (comparison with negative control [NC] group); †P < .05 (comparison with LPS control group). D, LPS-induced nuclear translocation of p65 was determined with immunofluorescence staining. The first row shows NF-αB staining, and the second row, NF-κB staining merged with DAPI staining. Fluorescent densities of activated NF-κB in nucleus were quantified (n = 3). ‡P < .01 (comparison with control group). †P < .05 (comparison with LPS control group). 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining is shown in blue; p65 in red.