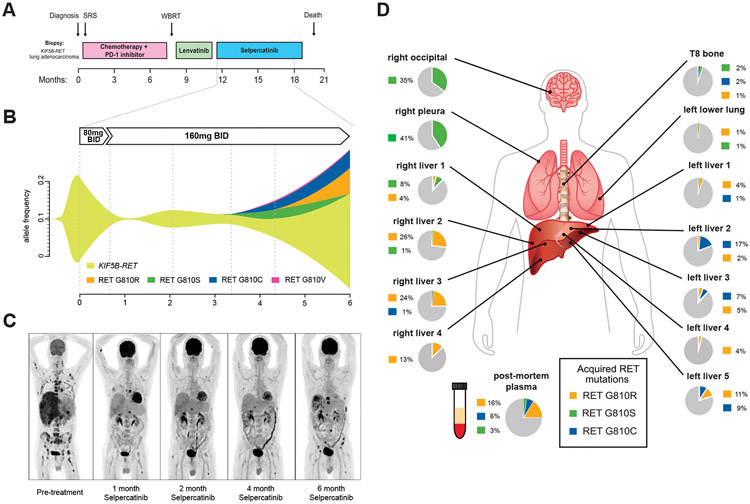
Figure 1.
Emergence of RET solvent front mutations after selpercatinib treatment in KIF5F-RET fusion-positive NSCLC. (A) Treatment timeline of the first patient with KIF5B-RET fusion-positive NSCLC; (B) plasma cell-free tumor DNA allelic frequencies of the founder KIF5B-RET fusion and emerging G810 substitution mutations (see also Supplementary Table 1); (C) PET imaging before and at the indicated times after initiating treatment with selpercatinib; (D) WGS of two liver lesions (right liver 3 and 4) to a depth of ×130 identified a KIF5B RET G810R encoding solvent front mutation in both lesions and no other RET mutations. Single RET amplicon-based sequencing to a depth of greater than ×10,000 identified mutations encoding KIF5B-RET G810S, G810C, and G810R mutations at varying allele frequencies (and no V804 mutations) throughout the metastatic lesions that were absent from a diagnostic lymph node biopsy and pre-selpercatinib plasma sample. SRS, stereotactic radiosurgery; WBRT, whole brain radiation therapy; RT, radiation therapy; mg, milligrams; BID, twice daily; TKI, tyrosine kinase inhibitor, RET, rearranged in transfection; WGS, whole genome sequencing; PET, positron emission tomography.