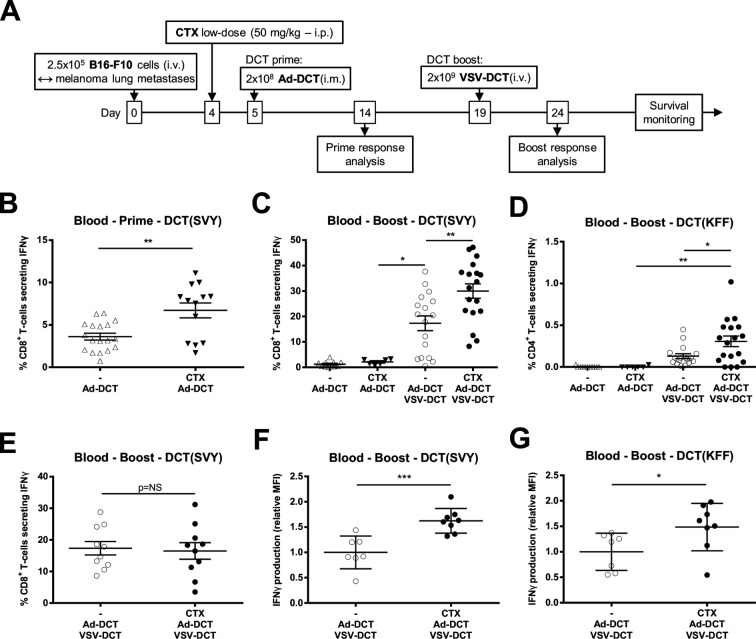
Figure 1.
Cyclophosphamide (CTX) increases the magnitude and quality of virus-based vaccination in tumor-bearing mice. (A) Timeline for treatment of mice bearing B16-F10 lung tumors. To measure T-cell reactivity against the tumor-associated antigen dopachrome tautomerase (DCT), circulating lymphocytes have been restimulated ex vivo with peptides corresponding to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-I and MHC-II-restricted immunodominant epitopes DCT(SVY) and DCT(KFF), respectively. (B) Frequency of circulating CD8+ T-cells reacting against DCT(SVY) 9 days after priming with the adenovirus (Ad)-DCT or CTX + Ad-DCT. (C) Frequency of reactive CD8+ T-cells 5 days after boosting in melanoma lung tumor-bearing animals treated with Ad-DCT, CTX + Ad-DCT, Ad-DCT + vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV)-DCT, and CTX + Ad-DCT + VSV-DCT. (D) Frequency of circulating CD4+ T-cells reacting against DCT(KFF) 5 days after boosting in tumor-bearing mice that received Ad-DCT, CTX + Ad-DCT, Ad-DCT + VSV-DCT, and CTX + Ad-DCT + VSV-DCT. (E) Frequency of interferon γ (IFNγ)+ CD8+ T-cells 5 days after boosting in tumor-free animals treated with Ad-DCT + VSV-DCT and CTX + Ad-DCT + VSV-DCT. (F, G) Production of IFNγ illustrated as relative mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) in (F) DCT-specific CD4+ and (G) CD8+ T-cells following treatment of tumor-bearing mice with Ad-DCT + VSV-DCT and CTX + Ad-DCT + VSV-DCT. Data displayed in (B–E) consist of pools of at least two distinct experiments; dot plots indicate mean±SEM. Data displayed in (F) and (G) are results from one representative experiment; dot plots indicate mean±SD. i.m., intramuscular; i.p., intraperitoneal; i.v. intravenous.