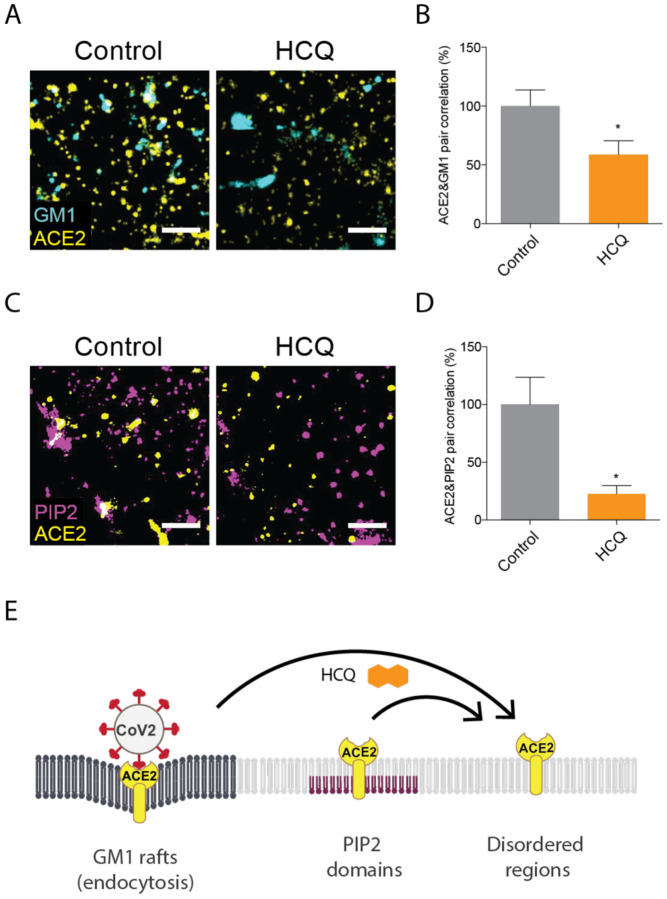
Fig. 3. Hydroxychloroquine moves ACE2 from GM1 rafts and PIP2 domains.
(A) Representative dSTORM super resolution images showing the effect of HCQ (50 μM) on the nanoscale localization of ACE2 (yellow) with GM1 rafts (cyan) after loading HEK293T cells with cholesterol (scale bars = 1 μm). (B) Percent of pair correlation (Fig. S3A) calculated at short distances (0–5 nm). HCQ decreased the pair correlation between ACE2 and GM1 rafts indicating a decrease in association between PLD and GM1 rafts. Data are expressed as mean ± s.e.m., *P ≤ 0.05, unpaired t-test, n=6. (C) Representative dSTORM super resolution images of ACE2 (yellow) and PIP2 domain (magenta) in HEK293T cells at normal cholesterol level after the treatment of HCQ (50 μM) (scale bars = 1 μm). (D) HCQ decreased the pair correlation between ACE2 and PIP2 domains indicating a decrease in association between PLD and PIP2 domains. Data are expressed as mean ± s.e.m., *P ≤ 0.05, unpaired t-test, n=5. (E) Model showing HCQ (orange hexagon) inducing translocation of ACE2 (yellow receptor) from GM1 rafts (dark grey lipids) in high cholesterol. HCQ disrupts ACE2 interaction with PIP2 domains causing ACE2 to translocate to the disordered region.